谷粒商城-分布式基础
上一级页面:springboot-gulimall
前言
本节的内容来自课后整理,听课的时候不用记录,主要是跟着思路敲代码。课后抽出时间整理一下笔记就好了。
学习笔记目录
鸣谢
笔记来源
感谢此项目:Brain map: 脑图、笔记 (gitee.com)
笔记来源2与开源项目支持
感谢大佬在记笔记这件事上提供的帮助:zsy0216/guli-mall: 尚硅谷-谷粒商城代码及文档https://www.yuque.com/zhangshuaiyin/guli-mall (github.com)
教学文档
感谢大佬的整理:Guli Mall(包含代码、课件、sql).rar

所有文档资料,老乡点个赞再走!
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/18FuF760AYt3kILGWCmXVEA
提取码:yyds参考、引用、致谢
感谢大佬的整理:Guli Mall(包含代码、课件、sql).rar

所有文档资料,老乡点个赞再走!
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/18FuF760AYt3kILGWCmXVEA
提取码:yyds谷粒商城基础篇
一、项目简介
1.1 项目背景
1.2 电商模式
市面上有 5 种常见的电商模式 B2B、B2B、C2B、C2C、O2O
1.2.1 B2B 模式
B2B(Business to Business),是指商家和商家建立的商业关系,如 阿里巴巴,
1.2.2 B2C 模式
B2C(Business to Consumer) 就是我们经常看到的供应商直接把商品买个用户,即 “商对客” 模式,也就是我们呢说的商业零售,直接面向消费销售产品和服务,如苏宁易购,京东,天猫,小米商城
1.2.3 C2B 模式
C2B (Customer to Business),即消费者对企业,先有消费者需求产生而后有企业生产,即先有消费者提出需求,后又生产企业按需求组织生产
1.2.4 C2C 模式
C2C (Customer to Consumer) 客户之间吧自己的东西放到网上去卖 如 淘宝 咸鱼
1.2.5 O2O 模式
O 2 O 即 Online To Offline,也即将线下商务的机会与互联网结合在一起,让互联网成为线下交易前台,线上快速支付,线下优质服务,如:饿了吗,美团,淘票票,京东到家
1.3 谷粒商城
谷粒商城是一个 B2C 模式的电商平台,销售自营商品给客户
1.4 项目架构图
1、项目微服务架构图

2、微服务划分图

1.5 项目技术&特色
- 前后分离开发,并开发基于 vue 的 后台管理系统
- SpringCloud 全新的解决方案
- 应用监控、限流、网关、熔断降级、等分布式方案,全方位涉及
- 透彻讲解分布式事务,分布式锁等分布式系统的难点
- 压力测试与性能优化
- 各种集群技术的区别以及使用
- CI/CD 使用
1.6 项目前置要求
学习项目的前置知识
- 熟悉 SpringBoot 以及常见整合方案
- 了解 SpringCloud
- 熟悉 git maven
- 熟悉 linux、redis docker 基本操作
- 了解 html,css,js,vue
- 熟练使用 idea 开发项目
二、分布式基础概念
2.1 微服务
微服务架构风格,就像是把一个单独的应用程序开发成一套小服务,每个小服务运行在自己的进程中,并使用轻量级机制通信,通常是 HTTP API 这些服务围绕业务能力来构建, 并通过完全自动化部署机制来独立部署,这些服务使用不同的编程语言书写,以及不同数据存储技术,并保持最低限度的集中式管理
简而言之,拒绝大型单体应用,基于业务边界进行服务拆分,每个服务独立部署运行。

2.2 集群&分布式&节点
集群是个物理状态,分布式是个工作方式
只要是一堆机器,也可以叫做集群,他不是不是一起协作干活,这谁也不知道,
《分布式系统原理与范型》定义:
“分布式系统是若干独立计算机的集合,这些计算机对于用户来说像但各相关系统”
分布式系统 (distributed system) 是建立网络之上的软件系统
分布式是指讲不通的业务分布在不同的地方
集群实质是将几台服务器集中在一起,实现同一业务
例如:京东是一个分布式系统,众多业务运行在不同的机器上,所有业务构成一个大型的业务集群,每一个小的业务,比如用户系统,访问压力大的时候一台服务器是不够的,我们就应该将用户系统部署到多个服务器,也就是每个一业务系统也可以做集群化
分布式中的每一个节点,都可以做集群,而集群并不一定就是分布式的
节点:集群中的一个服务器
2.3 远程调用
在分布式系统中,各个服务可能处于不同主机,但是服务之间不可避免的需要互相调用,我们称之为远程调用
SpringCloud 中使用 HTTP+JSON 的方式来完成远程调用

2.4 负载均衡

分布式系统中,A 服务需要调用 B 服务,B 服务在多台机器中都存在, A 调用任意一个服务器均可完成功能
为了使每一个服务器都不要太或者太闲,我们可以负载均衡调用每一个服务器,提升网站的健壮性
常见的负载均衡算法:
轮询:为第一个请求选择键康齿中的每一个后端服务器,然后按顺序往后依次选择,直到最后一个,然后循环
最小连接:优先选择链接数最少,也就是压力最小的后端服务器,在会话较长的情况下可以考虑采取这种方式
2.5 服务注册/发现&注册中心
A 服务调用 B 服务, A 服务不知道 B 服务当前在哪几台服务器上有,那些正常的,哪些服务已经下线,解决这个问题可以引入注册中心

如果某些服务下线,我们其他人可以实时的感知到其他服务的状态,从而避免调用不可用的服务
2.6 配置中心

每一个服务最终都有大量配置,并且每个服务都可能部署在多个服务器上,我们经常需要变更配置,我们可以让每个服务在配置中心获取自己的位置。
配置中心用来集中管理微服务的配置信息
2.7 服务熔断&服务降级
在微服务架构中,微服务之间通过网络来进行通信,存在相互依赖,当其中一个服务不可用时,有可能会造成雪崩效应,要防止这种情况,必须要有容错机制来保护服务

1、服务熔断
- 设置服务的超时,当被调用的服务经常失败到达某个阈值,我们可以开启断路保护机制,后来的请求不再去调用这个服务,本地直接返回默认的数据
2、服务降级
- 在运维期间,当系统处于高峰期,系统资源紧张,我们可以让非核心业务降级运行,降级:某些服务部处理,或者简单处理【抛异常,返回NULL,调用 Mock数据,调用 FallBack 处理逻辑】
2.8 API 网关
在微服务架构中,API Gateway 作为整体架构的重要组件,他 抽象类服务中需要的公共功能,同时它提供了客户端负载均衡,服务自动熔断,灰度发布,统一认证,限流监控,日志统计等丰富功能,帮助我们解决很多 API 管理的难题

三、环境搭建
3.1 安装 linux虚拟机
下载&安装 VirtualBox https://www.virtualbox.org/ 要开启 CPU 虚拟化


CPU 查看

下载& 安装 Vagrant
https://app.vagrantup.com/boxes/search Vagrant 官方镜像仓库
https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html Vagrant下载
打开window cmd窗口,运行Vagrant init centos/7 ,即可初始化一个centos系统
运行vagrant up即可启动虚拟机。系统root用户的密码是vagrant
vagrant其他常用命令
vagrant ssh 自动使用 vagrant 用户连接虚拟机
vagrant upload source [destination] [name|id] 上传文件
https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/cli/init.html Vagrant 命令行
默认虚拟机的ip 地址不是固定ip 开发不方便
Vagrant 和 VirtualBox 版本有对应问题 都安装最新版本 则安装成功
修改 Vagrantfile
config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.56.10"
这里 ip 需要在 物理机下使用 ipconfig 命令找到

3.2 安装 docker
Docker 安装文档参考官网
3.2.1 卸载系统之前安装的 docker
Uninstall old versions
一步一步往下执行就行
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engineSET UP THE REPOSITORY
Install the yum-utils package (which provides the yum-config-manager utility) and set up the stable repository.
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repoINSTALL DOCKER ENGINE
- Install the latest version of Docker Engine and containerd, or go to the next step to install a specific version:
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioStart Docker
sudo systemctl start dockerVerify that Docker Engine is installed correctly by running the hello-world image.
sudo docker run hello-world设置docker开机自启动
sudo systemctl enable docker设置 Docker 镜像加速
登录 aliyun.com 在控制台找到容器镜像服务

3.3 docker 安装 mysql
3.3.1 下载镜像文件
docker pull mysql:5.73.3.2 创建实例并启动
# --name指定容器名字 -v目录挂载 -p指定端口映射 -e设置mysql参数 -d后台运行
sudo docker run -p 3306:3306 --name mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/log:/var/log/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \
-d mysql:5.7
####
-v 将对应文件挂载到主机
-e 初始化对应
-p 容器端口映射到主机的端口MySQL 配置
vi /mydata/mysql/conf/my.cnf 创建&修改该文件
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
init_connect='SET collation_connection = utf8_unicode_ci'
init_connect='SET NAMES utf8'
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci
skip-character-set-client-handshake
skip-name-resolve3.3.3 通过容器的 mysql 命令行工具连接

3.4 docker 安装 redis
3.4.1 下载镜像文件
docker pull redis
3.4.2 创建实例并启动
mkdir -p /mydata/redis/conf
touch /mydata/redis/conf/redis.conf
# 启动 同时 映射到对应文件夹
# 后面 \ 代表换行
docker run -p 6379:6379 --name redis \
-v /mydata/redis/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d redis redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf3.4.3 使用 redis 镜像执行 redis-cli 命令连接
docker exec -it redis redis-cli
持久化 默认 appendonly on 没有开启
vim /mydata/redis/conf/redis.conf
# 插入下面内容
appendonly yes3.5 开发环境统一
3.5.1 Maven
配置阿里云镜像
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>配置 jdk 1.8 编译项目
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>3.5.2 idea&VsCode
idea 安装 lombok、mybatisx插件 Translation插件 等等..
Vscode 安装开发必备插件
Vetur ——语法高亮,智能感知 包含格式化功能,Alt+Shift+F (格式化全文) ,Ctrl+K Ctrl+F (格式化选中代码,两个Ctrl需要同时按着) EsLint 一一 语法纠错 Auto Close Tag 一一 自动闭合HTML/XML标签 Auto Rename Tag 一一 自动完成另-侧标签的同步修改 JavaScript(ES6) code snippets 一一 ES6 语法智能提示以及快速输入,除j外还支持.ts, .jsx, .tsx, .html, .vue;省去了配置其支持各种包含is代码文件的时间
VsCode开发vue 常用插件
https://blog.csdn.net/yujing1314/article/details/90340647
3.5.3 安装配置 git
1、下载git
https://git-scm.com/
2、配置git 进入 git bash
# 配置用户名
git config --global user.name "user.name"
# 配置邮箱
git config --global user.email "username@email.com" # 注册账号使用的邮箱3、配置 ssh 免密登录
https://github.com/settings/keys
git bash 使用 ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "XXX@xxx.com" 命令 连续三次回车
一般用户目录下都会有
id_rsa 文件
id_rsa.pub 文件
或者 cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
登录进 github/gitee 设置 SSH KEY
使用 ssh -T git@gitee.com 测试是否成功
具体过程参考百度3.5.4 逆向工程使用
1、导入项目逆向工程
2、下载人人开源后台管理系统脚手架工程
- 导入工程,创建数据库
- 修改工程shiro依赖为SpringSecurity
- 删除部分暂时不需要的业务
3、下载人人开源后台管理系统vue端脚手架工程
- vscode 导入前端项目
- 前后端联调测试基本功能
四、MybatisPlus整合
4.1 配置环境
4.1.1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>4.2.2、配置数据源
配置数据源
导入数据库驱动
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java
<!--导入mysql驱动--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.17</version> </dependency>在application.yml配置数据源相关信息
spring: datasource: username: root password: root url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.10:3306/gulimall_pms driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver mybatis-plus: # mapper文件扫描 mapper-locations: classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml global-config: db-config: id-type: auto # 数据库主键自增
配置MyBatis-Plus包扫描:
使用@MapperScanner
告诉MyBatis-Plus,Sql映射文件位置
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.gulimall.product.dao") @SpringBootApplication public class GulimallProductApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(GulimallProductApplication.class, args); } }
具体过程参考官网: https://baomidou.com/guide/install.html#release
4.2 分页配置
@Configuration // 声明配置类
@EnableTransactionManagement // 开启注解
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.gulimall.product.dao") // 指定扫描包
public class MyBatisConfig {
/**
* 引入分页插件 拦截器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor = new PaginationInterceptor();
// 设置请求的页面大于最大页后操作, true调回到首页,false 继续请求 默认false
paginationInterceptor.setOverflow(true);
// 设置最大单页限制数量,默认 500 条,-1 不受限制
paginationInterceptor.setLimit(1000);
// 开启 count 的 join 优化,只针对部分 left join
paginationInterceptor.setCountSqlParser(new JsqlParserCountOptimize(true));
return paginationInterceptor;
}
}4.3 逻辑删除
说明:
只对自动注入的sql起效:
- 插入: 不作限制
- 查找: 追加where条件过滤掉已删除数据,且使用 wrapper.entity 生成的where条件会忽略该字段
- 更新: 追加where条件防止更新到已删除数据,且使用 wrapper.entity 生成的where条件会忽略该字段
- 删除: 转变为 更新
例如:
- 删除:
update user set deleted=1 where id = 1 and deleted=0 - 查找:
select id,name,deleted from user where deleted=0
步骤1:配置 application.yml
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto # 数据库主键自增
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)步骤2: 实体类字段上加上@TableLogic注解
/**
* 是否显示[0-不显示,1显示]
*/
@TableLogic(value = "1",delval = "0")
private Integer showStatus;五、SpringCloud Alibaba
5.1 SpringCloud Alibaba 简介
5.1.1、简介
Spring Cloud Alibaba 致力于提供微服务开发的一站式解决方案。此项目包含开发分布式应用微服务的必需组件,方便开发者通过 Spring Cloud 编程模型轻松使用这些组件来开发分布式应用服务。
依托 Spring Cloud Alibaba,您只需要添加一些注解和少量配置,就可以将 Spring Cloud 应用接入阿里微服务解决方案,通过阿里中间件来迅速搭建分布式应用系统。
5.1.2、为什么要使用 ?


SpringClouid的几大痛点:
SpringCloud部分组件停止维护和更新,给开发带来不便;
SpringCloud部分环境搭建复杂,没有完善的可视化界面,我们需要大量的二次开发和定制
SpringCloud配置复杂,难以上手,部分配置差别难以区分和合理应用
SpringCloud Alibaba的优势:
阿里使用过的组件经历了考验,性能强悍,设计合理,现在开源出来大家用
成套的产品搭配完善的可视化界面给开发运维带来极大的便利
搭建简单,学习曲线低。
结合SpringCloud Alibaba我们最终的技术搭配方案:
SpringCloud Alibaba - Nacos : 注册中心 (服务发现/注册)
SpringCloud AlibabaNacos: 配置中心 (动态配置管理)
SpringCloud - Ribbon: 负载均衡
SpringCloud - Feign: 声明式HTTP客户端(调用远程服务)
SpringCloud Alibaba - Sentinel: 服务容错(限流、降级、熔断)
SpringCloud - Gateway: API 网关 (webflux 编程模式)
SpringCloud - Sleuth:调用链监控
SpringCloud Alibaba - Seata: 原Fescar, 即分布式事务解决方案
5.2 SpringCloud Alibaba - Nacos [作为注册中心]
Nacos 是阿里巴巴开源的一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现,配置管理和服务管理平台,他是使用 java 编写的,需要依赖 java 环境
Nacos 文档地址: https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html
5.2.1、下载 nacos-server
https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases
5.2.2、启动 nacos-server
- cmd 运行startup.cmd 文件
- 访问localhost:8848/nacos/
- 使用默认的 nacos/nacos 登录

5.2.3、注册进入 nacos 中
1、首先,修改 pom.xml 文件,引入 Nacos Discovery Starter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>2、在应用的 /resource /application.properties 中配置 Nacos Server地址
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:88483、使用@EnableDiscoveryClient 开启服务注册发现功能
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class, args);
}
}4、启动应用、观察 nacos 服务列表是否已经注册上服务
注意每一个应用都应该有名字,这样才能往册上去。修改pplicaion.propertes文件
spring.application.name= service provider
server.port=80005、注册更多的服务上去,测试使用 feign 远程
Nacos 使用三步
1、导包
2、写配置,指定 nacos 地址,指定应用的名字
3、开启服务注册发现功能 @EnableDiscoveryClient
Feign 使用三步
1、导包 openfeign
2、开启 @EnableFeignClients 功能
3、编写接口,进行远程调用
5.3 SpringCloud Alibaba - Nacos [作为配置中心]
5.3.1、pom.xml 引入 Nacos Config Starter
<!--配置中心来做配置管理-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>5.3.2、在应用的 resource 下 bootstrap.properties
spring.application.name=gulimall-coupon
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:88485.3.3、在 nacos 中添加配置
选择右上角添加配置

Data ID 改成 gulimall-coupon.properties 默认规则 用户名.应用名.properties

5.3.4、在应用中使用@Value 和 @RefreshScope
@RefreshScope // 刷新对应controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("coupon/coupon")
public class CouponController {
@Autowired
private CouponService couponService;
@Value("${coupon.user.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${coupon.user.age}")
private Integer age;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public R test() {
return R.ok().put("name",name).put("age",age);
}5.3.5、进阶
1、核心概念
命名空间:
用于进行租户粒度的配置隔离。不同的命名空间下,可以存在相同的 Group 或 DatalD 的配置。Namespace 的常用场景之一是不同环境的配置的区分隔离,例如开发测试环境和生产环境的资源(如配置、服务)隔离等。
配置集
一组相关或者不相关的配置项的集合称为配置集。在系统中,一个配置文件通常就是一个配置集,包含了系统各个方面的配置。例如,一个配置集可能包含了数据源、线程池、日志级别等配置项。
配置集ID:
Nacos 中的某个配置集的 ID,配置集 ID 是组织划分配置的维度之一,Data ID 通常用于组织划分系统的配置集,一个系统或者应用可以包含多个配置集,一个系统应用可以包含多个配置集,每个配置集都可以被一个有意义的名称标识,Data ID 通常采用类 Java 包 如 ( com.taobao.tc.refund.log.level ) 的命名规则保证全局唯一性,此命名规则非强制
配置分组:
Nacos 中的一组配置集,是组织配置的维度之一,通过一个有意义的字符串,(如 Buy 或 Trade ) 对配置集进行分组,从而区分 Data ID 相同的配置集,当您在 Nacos 上创建一个配置时,如果未填写配置分组的名称,则配置分组的名称默认采用,DEFAULT_GROUP 配置分组的常见场景,不同的应用或组件采用了相同的配置类型,如 database_url 配置和 MQ_topic 配置
bootstrap.properties 配置
spring.application.name=gulimall-coupon # 服务的名称
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848 # 服务注册地址
spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=ae34901c-9215-4409-ae61-c6b8d6c8f9b0 # 命名空间地址
#spring.cloud.nacos.config.group=111 # 对应分组
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].data-id=datasource.yml # 配置集指定data_id
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].group=dev # 配置集指定 group 分组
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].refresh=true # 是否动态刷新 在配置中心修改后 微服务自动刷新相关解释
/**
* 1、如何使用 Nacos作为配置中心统一管理配置
* 1.1 引入依赖
* <dependency>
* <groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
* <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
* </dependency>
* 1.2 创建一个bootstrap.properties
* spring.application.name=gulimall-coupon
* spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848
* 1.3 需要给配置中心默认添加一个叫 数据集 (Data Id) gulimall-coupon.properties 默认规则 用户名.应用名.properties
* 1.4 给 应用名.properties 添加任何配置
* 1.5 动态获取配置
* @RefreshScope: 动态获取并刷新配置
* @Value$("${配置项的名字}")
* 如果配置中心和当前应用的配置文件中都配置了相同的配置文件,优先使用配置中心的文件
*
* 2、细节
* 1、命名空间:配置隔离:
* 默认:public(保留空间);默认新增的所有配置都在 public 空间
* 1、开发 测试 生产 利用命名空间来做环境隔离
* 注意: 在bootstrap.properties配置上 需要使用哪个命名空间下的配置
* spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=b1e89ce0-784f-4a80-9de0-e9b080eeaca5
* 2、每一个微服务之间互相隔离配置,每一个微服务都创建自己的命名空间,只加载自己命名空间下的所有配置
*
*
* 2、配置集:所有配置的集合
*
* 3、配置集ID:类似文件名
* Data ID:类型文件名
*
* 4、配置分组:
* 默认所有的配置都属于 DEFAULT_GROUP
*
* 每个微服务创建自己的命名空间,使用配置分组区分环境,dev、test、prod
*
* 3、同时加载多个配置集
* 1、微服务任何配置信息,任何配置文件多可以放在配置中心中
* 2、只要在 bootstrap.properties 说明加载配置中心中哪些配置文件即可
* 3、@Value,@ConfigurationProperties...
* 以前SpringBoot的任何方式从配置文件中获取值,都能使用
* 配置中心有的优先使用配置中心的
* @author gcq
* @Create 2020-10-16
*/5.4 SpringCloud Alibaba-Sentinel
1、简介
1、服务降级限流
什么是熔断:
A 服务调用 B 服务的某个功能,由于网络不稳定问题,或者 B 服务卡机,导致功能时间超长,如果这样子的次数太多,我们可以直接将 B 断路了,(A 不在请求 B 接口)凡是调用 B 服务的直接返回降级数据,不必等待 B 的 超时执行,这样 B 的故障问题,就不会级联影响到 A。
什么是降级:
整个网站处于流量高峰期服务器压力剧增,根据当前自身业务情况以及流量,对一些服务和页面进行有策略的降级/停止服务,所有的调用直接返回降级数据以此缓解服务器资源的压力,以保证核心业务的正常运行,同时也保持了客户和大部分客户等到正确的响应
异同:
相同点
1、为了保证集群大部分服务的可用性和可靠性,防止崩溃,牺牲小我
2、用户最终都是体验到某个功能不可用
不同点:
1、熔断是被调用方的故障,触发系统的主动规则
2、降级是基于全局的考虑停止一些正常服务,释放资源
什么是限流
对打入的服务的请求流量进行控制,使服务能够承担不超过自己能力的流量压力
2、Sentinel 简介
官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D
项目文档:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel
随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。Sentinel 以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
- 丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、集群流量控制、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
- 完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
- 广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
- 完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展接口。您可以通过实现扩展接口来快速地定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配动态数据源等。
Sentinel 的主要特性:

Sentinel 分为两个部分:
- 核心库(Java 客户端)不依赖任何框架/库,能够运行于所有 Java 运行时环境,同时对 Dubbo / Spring Cloud 等框架也有较好的支持。
- 控制台(Dashboard)基于 Spring Boot 开发,打包后可以直接运行,不需要额外的 Tomcat 等应用容器。
Sentinel 基本概念:
- 资源
- 资源是 Sentinel 的关键概念。它可以是 Java 应用程序中的任何内容,例如,由应用程序提供的服务,或由应用程序调用的其它应用提供的服务,甚至可以是一段代码。在接下来的文档中,我们都会用资源来描述代码块。
- 只要通过 Sentinel API 定义的代码,就是资源,能够被 Sentinel 保护起来。大部分情况下,可以使用方法签名,URL,甚至服务名称作为资源名来标示资源。
- 规则
- 围绕资源的实时状态设定的规则,可以包括流量控制规则、熔断降级规则以及系统保护规则。所有规则可以动态实时调整。
2、Hystrix 与 Sentinel 比较

3、整合 Feign 和 Sentinel 测试熔断降级
熔断降级官网解释:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E7%86%94%E6%96%AD%E9%99%8D%E7%BA%A7
Spring- Cloud整合Sentinel和Feign:https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/wiki/Sentinel
pom.xml
<!-- 导入sentinel依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--导入openFeign -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>application.properties
## sentinel与项目间的通信端口
spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.port=8719
## sentinel端口设置
spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.dashboard=localhost:8333
## 暴露信息
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=*
## 配置文件打开 Sentinel 对 Feign 的支持
feign.sentinel.enabled=true开启后,在微服务中调用远程服务,Sentinel 就会记录微服务之间的调用,从而对远程调用进行设置熔断降级等。
请求设置

设置流控规则

Feign设置

结果

4、整合 Sentinel 测试限流
官网Spring-Cloud 整合:https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/wiki/Sentinel
Pom.xml
参考 3、整合 Feign 和 Sentinel 测试熔断降级
控制台:

超过单继阈值,返回自定义请求结果
实现方式:
/**
1、代码
* try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("resourceName")) {
* }(BlockedException e){}
* 2、基于注解
* @SentinelResource(value = "getCurrentSeckillSkusSource",blockHandler = "BlockHandler")
* 无论1/2方式一定要配置限流以后的默认返回
* url可以设置统一返回
**/具体实现方式参考官网给出文档:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8
5、Sentinel网关限流
官网文档:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E7%BD%91%E5%85%B3%E9%99%90%E6%B5%81
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-gateway</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>启动Sentinle1.7.1 后比原先的1.6.1多个一个功能

您可以在 GatewayCallbackManager 注册回调进行定制:
setBlockHandler:注册函数用于实现自定义的逻辑处理被限流的请求,对应接口为BlockRequestHandler。默认实现为DefaultBlockRequestHandler,当被限流时会返回类似于下面的错误信息:Blocked by Sentinel: FlowException。
@Configuration
public class SentinelGatewayConfig {
public SentinelGatewayConfig() {
GatewayCallbackManager.setBlockHandler(new BlockRequestHandler() {
// 网关限流了 就会回调
@Override
public Mono<ServerResponse> handleRequest(ServerWebExchange serverWebExchange, Throwable throwable) {
R error = R.error(BizCodeEnume.TO_MANY_REQUEST.getCode(), BizCodeEnume.TO_MANY_REQUEST.getMsg());
String errorJson = JSON.toJSONString(error);
Mono<ServerResponse> body = ServerResponse.ok().body(Mono.just(errorJson), String.class);
return body;
}
});
}
}5.5 SpringCloud Alibaba-Seata
1、简介
Seata 是一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,致力于提供高性能和简单易用的分布式事务服务。Seata 将为用户提供了 AT、TCC、SAGA 和 XA 事务模式,为用户打造一站式的分布式解决方案。
https://seata.io/zh-cn/index.html
2、核心概念
TC (Transaction Coordinator) - 事务协调者
维护全局和分支事务的状态,驱动全局事务提交或回滚。
TM (Transaction Manager) - 事务管理器
定义全局事务的范围:开始全局事务、提交或回滚全局事务。
RM (Resource Manager) - 资源管理器
管理分支事务处理的资源,与TC交谈以注册分支事务和报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务提交或回滚。
5.6 SpringCloud Alibaba-OSS
5.6.1、简介
对象存储服务 阿里云对象存储服务(Object Storage Service,简称 OSS),是阿里云提供的海量、安全、低成本、高可靠的云存储服务。您可以在任何应用、任何时间、任何地点存储和访问任意类型的数据。

5.6.2、使用步骤
使用 Java 上传文件
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/32011.html?spm=a2c4g.11186623.6.915.56196d39rr96Ll
来自官网实例 - 上传文件流
@Test
public void testUpload() throws FileNotFoundException {
// Endpoint以杭州为例,其它Region请按实际情况填写。
String endpoint = "http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// 云账号AccessKey有所有API访问权限,建议遵循阿里云安全最佳实践,创建并使用RAM子账号进行API访问或日常运维,请登录 //https://ram.console.aliyun.com 创建。
String accessKeyId = "<yourAccessKeyId>";
String accessKeySecret = "<yourAccessKeySecret>";
// 创建OSSClient实例。
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder().build(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);
// 上传文件流。
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("<yourlocalFile>");
ossClient.putObject("<yourBucketName>", "<yourObjectName>", inputStream);
// 关闭OSSClient。
ossClient.shutdown();
System.out.println("上传成功");
}需要填写 AccesskeyId 以及 Secret 同时也要指定文件位置 以及文件名字
最终上传结果

5.6.3、 抽取成一个单独的第三方服务?OSS
官网文档
https://github.com/alibaba/aliyun-spring-boot/blob/master/aliyun-spring-boot-samples/aliyun-oss-spring-boot-sample/README-zh.md
新建项目 gulimall-third-party
pom 配置
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alicloud-oss</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- springCloudAlibaba -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>application.yml 配置 accessKey、secretKey、endpoint
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
alicloud:
access-key: LTAI4GE22ckocpNBfd36zkxJ
secret-key: qDFrQ6cxZqc4DwxoWx5K2aosXXj0Go
oss:
endpoint: oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com ## 地域节点
bucket: gulimall-oss01 # 桶列表
application:
name: gulimall-third-party
server:
port: 300005.6.4、Web端上传介绍
阿里云对象存储-普通上传方式:

用户提交文件到服务器,服务器将文件提交到 OSS 对象存储
和数据直传到OSS相比,以上方法有三个缺点:
- 上传慢:用户数据需先上传到应用服务器,之后再上传到OSS。网络传输时间比直传到OSS多一倍。如果用户数据不通过应用服务器中转,而是直传到OSS,速度将大大提升。而且OSS采用BGP带宽,能保证各地各运营商之间的传输速度。
- 扩展性差:如果后续用户多了,应用服务器会成为瓶颈。
- 费用高:需要准备多台应用服务器。由于OSS上传流量是免费的,如果数据直传到OSS,不通过应用服务器,那么将能省下几台应用服务器。
阿里云对象存储-服务端签名后直传:

流程介绍
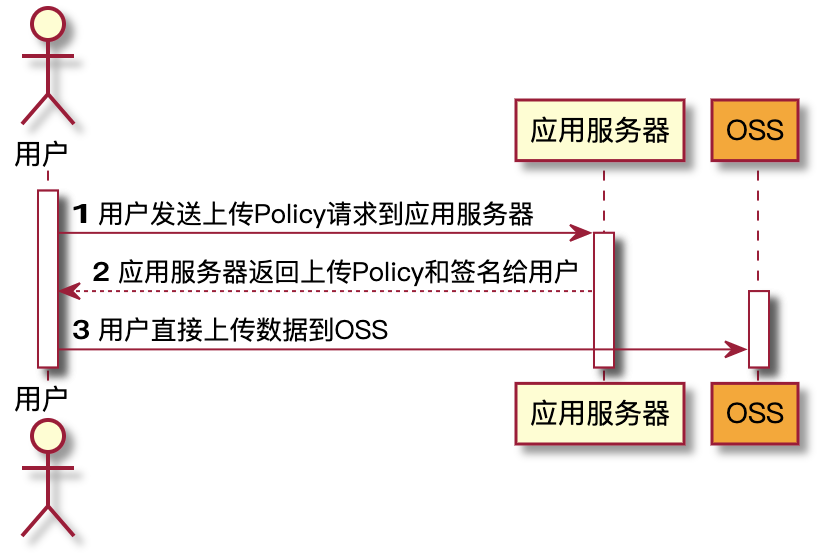
背景
采用JavaScript客户端直接签名(参见JavaScript客户端签名直传)时,AccessKey ID和AcessKey Secret会暴露在前端页面,因此存在严重的安全隐患。因此,OSS提供了服务端签名后直传的方案。
Web端向服务端请求签名,然后直接上传,不会对服务端产生压力,而且安全可靠。服务端签后直传
六、SpringCloud
6.1 Feign 声明式远程调用
6.1.1、简介
Feign 是一个声明式的 HTTP 客户端,他的目的就是让远程调用更加简单,Feign提供了 HTTP请求的模板,通过编写简单的接口和插入注解,就可以定义好的 HTTP 请求参数、格式、地址等信息
Feign 整合了 Ribbon(负载均衡)和 Hystrix(服务熔断),可以让我们不再需要显示地使用这两个组件
SpringCloud - Feign,在 NetflixFeign 的基础上扩展了对 SpringMVC 注解的支持,在其实现下,我们只需创建一个接口并用注解的方式来配置它,即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定。简化了 SpringCloud - Ribbon 自行封装服务调用客户端的开发量。
6.1.2、使用
1、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>2、开启 feign 功能
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.atguigu.gulimall.pms.feign") // 指定feign包位置3、声明远程接口
@FeignClient("gulimall-ware")
public interface WareFeignService {
@PostMapping("/ware/waresku/skus")
public Resp<List<SkuStockVO>> skuWareInfos(@RequestBody List<Long> skuIds)
}总结
/**
* 1、想要远程调用别的服务
* 1.1 引入open-feing
* 1.2 编写一个接口,告诉SpringCloud这个接口需要调用的远程服务
* 1.2.1 生命接口的每一个方法都是调用远程服务的那个请求
* 1.3 开启远程调用功能
*/6.2 Gateway
6.2.1、简介
网关作为流浪入口,常用功能包括路由转发,权限效验,限流控制等,而 SpringCloud GateWay作为 SpringCloud 官方推出的第二代网关框架,取代了 Zull 网关
网上测试 三种网关对应请求数

网关提供 API 全托管服务,丰富的 API 管理功能,辅助企业管理大规模的 API,以降低管理成本和安全风险、包括协议适配、协议转发、安全策略、防刷、流量、监控日志等功能
Spring Cloud GateWay 旨在提供一种简单有效的方式来对 API 进行路由,并为他们提供切面,列如、安全性、监控/指标 和弹性等
官网文档地址
6.3 Sleuth+Zipkin 服务链路追踪
1、为什么用
微服务架构是一个分布式架构,它按业务划分服务单元,一个分布式系统往往有很多个服务单元。由于服务单元数量众多,业务的复杂性,如果出现了错误和异常,很难去定位。主要体现在,一个请求可能需要调用很多个服务,而内部服务的调用复杂性,决定了问题难以定位。所以微服务架构中,必须实现分布式链路追踪,去跟进一个请 求到底有哪些服务参与,参与的顺序又是怎样的,从而达到每个请求的步骤清晰可见,出了问题,很快定位。
链路追踪组件有Google 的Dapper, Twitter 的Zipkin,以及阿里的Eagleeye(鹰眼)等,它们都是非常优秀的链路追踪开源组件。
2、基本术语
- Span (跨度) :基本工作单元,发送一个远程调度任务就会产生一个Span, Span 是一个64位ID唯一标识的,Trace 是用另一个64ID唯一标识的,Span 还有其他数据信息,比如摘要、时间戳事件、Span的ID、 以及进度ID。
- Trace (跟踪) :一系列Span组成的一个树状结构。请求一个微服务系统的API接口,这个API接口,需要调用多个微服务,调每个微服务都会产生一个新的Span,所有由这个请求产生的Span组成了这个Trace
- Annotation (标注) :用来及时记录一个事件的,一些核心注解用来定义一个请求的开始和结束。这些注解包括以下:
- csClient Sent客户端发送一 个请求,这个注解描述了这个Span的开始
- srServer Received -服务端获得请求并准备开始处理它,如果将其sr诚去cs时间戳便可得到网络传输的时间。
- ssServer Sent(服务端 发送响应) -该注解表明请求处理的完成(当请求返回客户端),如果ss的时间戳诚去sr时间戳,就可以得到服务器请求的时间。
- crClient Received (客 户端接收响应)此时Span的结束,如果cr的时间戳诚去cs时间戳便可以得到整个请求所消耗的时间。
官方文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-sleuth/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/html/
如果调用顺序是这样的
3、整合 Sleuth
1、服务提供者与消费者导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
</dependency>2、打开 debug 日志
3、发起一次远程调用,观察控制台
4、整合 zipkin 可视化观察
通过 Sleuth 产生的调用链监控信息,可以得知微服务之间的调用链路,但监控信息只输出到控制台不方便查看,我们需要一个图形化的工具 -Zipkin ,Zipkin 是 Twitter 开源的分布式跟踪系统,主要用来收集系统的时序数据,从而追踪链路的调用问题,zipkin 官网地址如下:
https://zipkin.io/

1、docker 安装 zipkin服务器
docker run -d -p 9411:9411 openzipkin/zipkin2、pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>3、application.yml
# zipkin查询服务器实例的URL
spring.zipkin.base-url=http://192.168.56.10:9411/
# 不查询自己
spring.zipkin.discovery-client-enabled=false
# 发送类型
spring.zipkin.sender.type=web
# 应用采样的请求概率
spring.sleuth.sampler.probability=15、Zipkin 数据持久化
Zipkin默认是将监控数据存储在内存的,如果Zipkin挂掉或重启的话,那么监控数据就会丢失。所以如果想要搭建生产可用的Zipkin,就需要实现监控数据的持久化。而想要实现数据持久化,自然就是得将数据存储至数据库。好在Zipkin 支持将数据存储至:
内存(默认)
MySQL
Elasticsearch
Cassandra
Zipkin 数据持久化相关官方文档地址如下
七、前端开发基础知识
这个等以后深入学习在进行记录~~~~
7.1 VSCode 使用
Get
"http-get请求": {
"prefix": "httpget",
"body": [
"this.\\$http({",
"url: this.\\$http.adornUrl(''),",
"method: 'get',",
"params: this.\\$http.adornParams({})",
"}).then(({ data }) => {",
"})"],
"description": "httpGET请求"
},POST
"http-post请求": {
"prefix": "httppost",
"body": [
"this.\\$http({",
"url: this.\\$http.adornUrl(''),",
"method: 'post',",
"data: this.\\$http.adornData(data, false)",
"}).then(({ data }) => { });" ],
"description": "httpPOST请求"
}7.2 ES6
7.3 Node.js
7.4 Vue
7.4.5 整合 Element UI
1、安装
npm i element-ui -S
2、引入 Element
main.js 中引入以下内容
import Vue from 'vue';
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'; // 引入静态资源文件
import App from './App.vue';
Vue.use(ElementUI);
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
});7.5 Babel
7.6 Webpack
八、商品服务&三级分类
8.1 基础概念
8.1.1、三级分类

一级分类查出二级分类数据,二级分类中查询出三级分类数据
数据库设计

8.1.2、SPU 和 SKU
SPU:Standard Product Unit (标准化产品单元)
是商品信息聚合的最小单位,是一组可复用,易检索的标准化信息的组合,该集合描述了一个产品的特性


IPhoneX 是 SPU,MI8 是 SPU
IPhoneX 64G 黑曜石 是 SKU
MIX8 + 64G 是 SKU
SKU: Stock KeepingUnit (库存量单位)
8.1.3、基本属性 【规格参数】与 销售属性
每个分共下的商共享规格参数、与销售属性,只是有些商品不一定更用这个分类下全部的属性:
属性是以三级分类组织起来的
规格参数中有些是可以提供检索的
规格参数也是基本属性,他们具有自己的分组
属性的分组也是以三级分类组织起来的
属性名确定的,但是值是每一个商品不同来决定的
【属性分组-规格参数-销售属性-三级分类】关联关系

SPU-SKU-属性表

8.1.4、接口文档位置
https://easydoc.xyz/s/78237135/ZUqEdvA4/hKJTcbfd
8.1.5、 Object 划分
1、PO (persistant object) 持久化对象
po 就是对应数据库中某一个表的一条记录,多个记录可以用 PO 的集合,PO 中应该不包含任何对数据库到操作
2、DO ( Domain Object) 领域对象
就是从现实世界抽象出来的有形或无形的业务实体
3、TO (Transfer Object) 数据传输对象
不同的应用程序之间传输的对象
4、DTO (Data Transfer Object) 数据传输对象
这个概念来源于 J2EE 的设计模式,原来的目的是为了 EJB的分布式应用提供粗粒度的数据实体,以减少分布式调用的次数,从而提高分数调用的性能和降低网络负载,但在这里,泛指用于展示层与服务层之间的数据传输对象
5、VO(value object) 值对象
通常用于业务层之间的数据传递,和 PO 一样也是仅仅包含数据而已,但应是抽象出的业务对象,可以和表对应,也可以不,这根据业务的需要,用 new 关键字创建,由 GC 回收
view Object 试图对象
接受页面传递来的数据,封装对象,封装页面需要用的数据
6、BO(business object) 业务对象
从业务模型的角度看,见 UML 原件领域模型中的领域对象,封装业务逻辑的, java 对象,通过调用 DAO 方法,结合 PO VO,进行业务操作,business object 业务对象,主要作用是把业务逻辑封装成一个对象,这个对象包括一个或多个对象,比如一个简历,有教育经历,工作经历,社会关系等等,我们可以把教育经历对应一个 PO 、工作经验对应一个 PO、 社会关系对应一个 PO, 建立一个对应简历的的 BO 对象处理简历,每 个 BO 包含这些 PO ,这样处理业务逻辑时,我们就可以针对 BO 去处理
7、POJO ( plain ordinary java object) 简单无规则 java 对象
传统意义的 java 对象,就是说一些 Object/Relation Mapping 工具中,能够做到维护数据库表记录的 persisent object 完全是一个符合 Java Bean 规范的 纯 java 对象,没有增加别的属性和方法,我们的理解就是最基本的 Java bean 只有属性字段 setter 和 getter 方法
POJO 时是 DO/DTO/BO/VO 的统称
8、DAO(data access object) 数据访问对象
是一个 sun 的一个标准 j2ee 设计模式,这个模式有个接口就是 DAO ,他负持久层的操作,为业务层提供接口,此对象用于访问数据库,通常和 PO 结合使用,DAO 中包含了各种数据库的操作方法,通过它的方法,结合 PO 对数据库进行相关操作,夹在业务逻辑与数据库资源中间,配合VO 提供数据库的 CRUD 功能
8.2 三级分类接口编写
// 返回查询所有分类以及子子分类,以树形结构组装起来
List<CategoryEntity> listWithTree();实现类:
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> listWithTree() {
// 1、查出所有分类 设置为null查询全部
List<CategoryEntity> entities = baseMapper.selectList(null);
// 2、组装成父子的树形结构
List<CategoryEntity> levelList = entities.stream().filter(categoryEntity -> {
// parentCid ==0 为父目录默认0
return categoryEntity.getParentCid() == 0;
}).map(menu -> {
// 设置二三级分类 递归
menu.setChildren(getChildrens(menu,entities));
return menu;
}).sorted((menu1, menu2) -> {
// 排序 Sort字段排序
return (menu1.getSort() == null ? 0 : menu1.getSort()) - (menu2.getSort() == null ? 0 : menu2.getSort());
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return levelList;
}
/**
* 递归查询子分类
* @param root 当前category对象
* @param all 全部分类数据
* @return
*/
private List<CategoryEntity> getChildrens(CategoryEntity root, List<CategoryEntity> all) {
List<CategoryEntity> collect = all.stream().filter(categoryEntity -> {
// 遍历所有的category对象的父类id = 等于root的分类id 说明是他的子类
return categoryEntity.getParentCid() == root.getCatId();
}).map(menu -> {
// 1、递归遍历菜单
menu.setChildren(getChildrens(menu, all));
return menu;
}).sorted((menu1, menu2) -> {
// 2、菜单排序
return (menu1.getSort() == null ? 0 : menu1.getSort()) - (menu2.getSort() == null ? 0 : menu2.getSort());
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect;
}跨域
跨域:指的是浏览器不能执行其他网站的脚本。它是由浏览器的同源策略造成的,是浏览器对javascript施加的安全限制。
同源策略:是指协议,域名,端口都要相同,其中有一个不同都会产生跨域;
下图详细说明了 URL 的改变导致是否允许通信

跨域流程

浏览器发请求都要实现发送一个请求询问是否可以进行通信 ,我直接给你返回可以通信不就可以了吗?
相关资料参考:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Access_control_CORS
解决跨越( 一 ) 使用nginx部署为同一域
开发过于麻烦,上线在使用

解决跨域 ( 二 )配置当次请求允许跨域
1、添加响应头
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: 支持哪些来源的请求跨域
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: 支持哪些方法跨域
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: 跨域请求默认不包含cookie,设置为true可以包含cookie
Access-Control-Expose-Headers: 跨域请求暴露的字段
CORS请求时, XML .HttpRequest对象的getResponseHeader()方法只能拿到6个基本字段: CacheControl、Content-L anguage、Content Type、Expires、
Last-Modified、 Pragma。 如果想拿到其他字段,就必须在Access-Control-Expose-Headers里面指定。
Access-Control-MaxAge: 表明该响应的有效时间为多少秒。在有效时间内,浏览器无须为同一-请求再次发起预检请求。请注意,浏览器自身维护了一个最大有效时间,如果该首部字段的值超过了最大有效时间,将不会生效。
网关配置文件
- id: product_route
uri: lb://gulimall-product
predicates:
- Path=/api/product/**
filters:
- RewritePath=/api/(?<segment>/?.*),/$\{segment}
- id: admin_route
uri: lb://renren-fast # lb负载均衡
predicates:
- Path=/api/** # path指定对应路径
filters: # 重写路径
- RewritePath=/api/(?<segment>/?.*), /renren-fast/$\{segment}跨越设置
请求先发送到网关,网关在转发给其他服务 事先都要注册到注册中心
@Configuration
public class GulimallCorsConfiguration {
@Bean
public CorsWebFilter corsWebFilter() {
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = new CorsConfiguration();
// 配置跨越
corsConfiguration.addAllowedHeader("*"); // 允许那些头
corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod("*"); // 允许那些请求方式
corsConfiguration.addAllowedOrigin("*"); // 允许请求来源
corsConfiguration.setAllowCredentials(true); // 是否允许携带cookie跨越
// 注册跨越配置
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**",corsConfiguration);
return new CorsWebFilter(source);
}
}8.2.1 树形展示三级分类数据
1、用到的前端组件 Tree 树形控件

<el-tree :data="data" :props="defaultProps" @node-click="handleNodeClick"></el-tree>
<!--
data 展示数据
props 配置选项
children 指定子树为节点对象的某个属性值
label 指定节点标签为节点对象的某个属性值
disabled 节点选择框是否禁用为节点对象的某个属性值
@node-click 节点被点击时的回调
-->配置静态数据就能显示出对应的效果
2、编写方法获取全部菜单数据
getMenus() {
this.$http({
// 请求接口见上面
url: this.$http.adornUrl("/product/category/list/tree"),
method: "get"
}).then(({ data }) => {
console.log("返回的菜单数据" + data.data);
this.menus = data.data;
});
}3、最终展示结果 ( append ,edit 会在后面介绍)

8.2.2 逻辑删除&删除效果细化
效果图


1、节点的内容支持自定义,可以在节点区添加按钮或图标等内容
<el-button
v-if="node.childNodes.length == 0"
type="text"
size="mini"
@click="() => remove(node, data)"
> Delete</el-button>
<!--
v-if="node.childNodes.length == 0" 没有子节点可以删除
type 对应类型
size 大小
@click 点击后出发的方法 此处使用了 箭头函数
-->2、前端remove方法进行删除
remove(node, data) {
this.$confirm(`是否删除【${data.name}】菜单 ? `, "提示", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
cancelButtonText: "取消",
type: "warning"
})
.then(() => {
// 拿到当前节点的catId
var ids = [data.catId];
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl("/product/category/delete"),
method: "post",
data: this.$http.adornData(ids, false)
}).then(({ data }) => {
this.$message({
message: "菜单删除成功",
type: "success"
});
// 刷新菜单
this.getMenus();
// 设置默认需要展开的菜单
/**
default-expanded-keys 默认展开节点的 key 数组
*/
this.expandedKey = [node.parent.data.catId];
console.log(node.parent.data.catId);
});
})
.catch(() => {});
console.log("remove", node, data);
}3、后端接口 -- 逻辑删除配置
3.1 第一种方式 mybatisplus 逻辑删除参考官网:https://baomidou.com/guide/logic-delete.html
在appliction.yml 中配置 myabtisplus 逻辑删除
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto # 数据库主键自增
logic-delete-value: 1 # 逻辑已删除值(默认为 1)
logic-not-delete-value: 0 # 逻辑未删除值(默认为 0)3.2 第二种方式 在 Entity中 使用注解
/**
是否为数据库表字段
默认 true 存在,false 不存在
标记为false 说明 该字段不在数据库
**/
@TableField(exist = false)
private List<CategoryEntity> children;4、Controller 实现 使用了代码生成器
/**
* 删除
* @RequestBody:获取请求体,必须发送post请求才有 get请求没有
* SpringMvc 自动将请求体的数据 ( json ) 转为对应的对象
*/
@RequestMapping("/delete")
public R delete(@RequestBody Long[] catIds){
// 1、检查当前删除的菜单,是否被别的地方应用
categoryService.removeMenuByIds(Arrays.asList(catIds));
return R.ok();
}
//Service 实现
@Override
public void removeMenuByIds(List<Long> asList) {
// 1、逻辑删除
baseMapper.deleteBatchIds(asList);
}8.2.3 新增效果&基本修改

1、前端组件 button 组件 Dialog 对话框
<!-- 层级小于2 才能新增 -->
<el-button
v-if="node.level <= 2"
type="text"
size="mini"
@click="() => append(data)"
>Append
</el-button>
<el-button type="text" size="mini" @click="() => edit(data)"
>edit
</el-button>
<!-- 上面组件在tree中-->
<el-dialog
:title="title"
:visible.sync="dialogVisible"
width="30%"
:before-close="handleClose"
:close-on-click-modal="false"
>
<el-form :model="category">
<el-form-item label="分类名称">
<el-input v-model="category.name" autocomplete="off"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="图标">
<el-input v-model="category.icon" autocomplete="off"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="计量单位">
<el-input
v-model="category.productUnit"
autocomplete="off"
></el-input>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
<span slot="footer" class="dialog-footer">
<el-button @click="dialogVisible = false">取 消</el-button>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitData">确 定</el-button>
</span>
</el-dialog>2、新增&修改
append(data) {
this.dialogVisible = true;
console.log("append", data);
this.category.name = "";
this.dialogType = "add";
this.title = "添加分类";
this.category.parentCid = data.catId;
this.category.catLevel = data.catLevel * 1 + 1;
this.category.name = "";
this.category.catId = null;
this.category.icon = "";
this.category.productUnit = "";
}, // 要修改的数据
edit(data) {
console.log("要修改的数据", data);
this.dialogType = "edit";
this.title = "修改分类";
this.dialogVisible = true;
// 发送请求获取最新的数据
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl(`/product/category/info/${data.catId}`),
method: "get"
}).then(({ data }) => {
// 请求成功
console.log("要回显的数据", data);
this.category.name = data.data.name;
this.category.catId = data.data.catId;
this.category.icon = data.data.icon;
this.category.productUnit = data.data.productUnit;
this.category.parentCid = data.data.parentCid;
});
},
submitData() {
if (this.dialogType == "add") {
// 进行新增
this.addCategory();
}
if (this.dialogType == "edit") {
// 进行修改
this.editCategory();
}
},
// 添加三级分类
addCategory() {
console.log("添加三级分类的数据", this.category);
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl("/product/category/save"),
method: "post",
data: this.$http.adornData(this.category, false)
}).then(({ data }) => {
this.$message({
message: "菜单保存成功",
type: "success"
});
// 关闭对话框
this.dialogVisible = false;
// 重新刷新数据
this.getMenus();
// 默认展开的菜单
this.expandedKey = [this.category.parentCid];
});
}, // 修改三级分类数据
editCategory() {
// 解构出单独的几个对象 用来提交
var { catId, name, icon, productUnit } = this.category;
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl("/product/category/update"),
method: "post",
data: this.$http.adornData({ catId, name, icon, productUnit }, false)
}).then(({ data }) => {
this.$message({
message: "菜单修改成功",
type: "success"
});
// 关闭对话框
this.dialogVisible = false;
// 重新刷新数据
this.getMenus();
// 默认展开的菜单
this.expandedKey = [this.category.parentCid];
});
},3、要考虑到的点 以及细节
- 添加完成后要把表单的数据进行清除,否则第二次打开任然会有上次表单提交剩下的数据 this.category.name = "";
- 修改和新增用的是同一个表单,因此在方法对话框中 动态的绑定了 :title="title" 标题 用于显示是新增还是修改
- 一个表单都是一个提交方法 因此在提交方法的时候进行了判断,根据变量赋值决定调用那个方法 this.dialogType = "add"; this.dialogType = "edit";
8.2.4 拖拽功能&数据收集&批量删除
效果演示

1、前端用的组件 Tree 树形控件 可拖拽节点
通过 draggable 属性可让节点变为可拖拽。
<el-tree
:expand-on-click-node="false"
:data="menus"
:props="defaultProps"
show-checkbox
node-key="catId"
:default-expanded-keys="expandedKey"
:draggable="draggable"
:allow-drop="allowDrop"
@node-drop="handleDrop"
ref="menuTree"
>
<!--
:expand-on-click-node 是否在点击节点的时候展开或者收缩节点 默认 true 则只有点箭头图标的时候才会展开或者收缩节点。
show-checkbox 节点是否可被选择
node-key 每个树节点用来做唯一标识的属性
default-expanded-keys 默认展开节点的节点
draggable 表示是否可以被拖拽 true&false
allow-drop 拖拽时判定目标节点能否被放置
node-drop 拖拽成功完成出发的事件
ref 该组件tree的引用
详细解释参考官网 https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/tree
-->2、主要业务逻辑 TODO:暂时不懂 回头再来看
allowDrop:
拖拽时判定目标节点能否被放置。type 参数有三种情况:'prev'、'inner' 和 'next',分别表示放置在目标节点前、插入至目标节点和放置在目标节点后
@node-drop
拽成功完成时触发的事件
共四个参数,依次为:被拖拽节点对应的 Node、结束拖拽时最后进入的节点、被拖拽节点的放置位置(before、after、inner)、event
allowDrop(draggingNode, dropNode, type) {
// 1、被拖动的当前节点以及所在的父节点总层次不能大于3
// 1) 被拖动节点的总层数
console.log("allowDrop", draggingNode, dropNode, type);
this.countNodeLevel(draggingNode.data);
// 当前正在拖动的节点 + 父节点所在的深度不大于3即可
let deep = Math.abs(this.maxLevel - draggingNode.level) + 1;
console.log("深度", deep);
if (type == "inner") {
return deep + dropNode.level <= 3;
} else {
return deep + dropNode.parent.level <= 3;
}
},
countNodeLevel(node) {
// 找到所有子节点,求出最大深度
if (node.children != null && node.children.length > 0) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.children.length; i++) {
if (node.children[i].catLevel > this.maxLevel) {
this.maxLevel = node.children[i].catLevel;
}
// 递归查找
this.countNodeLevel(node.children[i]);
}
}
}, handleDrop(draggingNode, dropNode, dropType, ev) {
console.log("handleDrop: ", draggingNode, dropNode, dropType);
// 1、当前节点最新的父节点
let pCid = 0;
let siblings = null;
if (dropType == "before" || dropType == "after") {
pCid =
dropNode.parent.data.catId == undefined
? 0
: dropNode.parent.data.catId;
siblings = dropNode.parent.childNodes;
} else {
pCid = dropNode.data.catId;
siblings = dropNode.childNodes;
}
// this.PCid = pCid
this.pCid.push(pCid);
// 2、当前拖拽节点的最新顺序
for (let i = 0; i < siblings.length; i++) {
if (siblings[i].data.catId == draggingNode.data.catId) {
// 如果遍历的是当前正在拖拽的节点
let catLevel = draggingNode.level;
if (siblings[i].level != draggingNode.level) {
// 当前结点的层级发生变化
catLevel = siblings[i].level;
// 修改它子节点的层级
this.updateChildNodeLevel(siblings[i]);
}
// 如果遍历当前正在拖拽的节点
this.updateNodes.push({
catId: siblings[i].data.catId,
sort: i,
parentCid: pCid
});
} else {
this.updateNodes.push({ catId: siblings[i].data.catId, sort: i });
}
}
// 3、当前拖拽节点的最新层级
console.log("updateNodes", this.updateNodes);
},
updateChildNodeLevel() {
if (node.childNodes.length > 0) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.childNodes.length; i++) {
var cNode = node.childNodes[i].data;
this.updateNodes.push({
catId: cNode.catId,
catLevel: node.childNodes[i].level
});
this.updateChildNodeLevel(node.childNodes[i]);
}
}
},3、批量删除
<el-button type="danger" @click="batchDelete">批量删除</el-button>batchDelete方法
batchDelete() {
let catIds = [];
let names = [];
// 返回目前被选中的节点所组成的数组
let checkedNodes = this.$refs.menuTree.getCheckedNodes();
console.log("被选中的元素", checkedNodes);
for (let i = 0; i < checkedNodes.length; i++) {
// 遍历节点数组 拿到需要的值
catIds.push(checkedNodes[i].catId);
names.push(checkedNodes[i].name);
}
this.$confirm(`是否批量删除【${names}】菜单 ? `, "提示", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
cancelButtonText: "取消",
type: "warning"
}).then(() => {
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl("/product/category/delete"),
method: "post",
data: this.$http.adornData(catIds, false)
}).then(({ data }) => {
this.$message({
message: "删除成功",
type: "success"
});
// 刷新菜单
this.getMenus();
});
});
},后端接口也是逻辑批量删除
void removeMenuByIds(List<Long> asList); //接收的是一个id数组总结:
前端用到的组件
Dialog 对话框、可拖拽节点、Switch 开关、Button 按钮、Tree组件(属性较多)
细节点:
没开启拖拽

开启拖拽:
通过 draggable 属性可让节点变为可拖拽。


九、商品服务&品牌管理
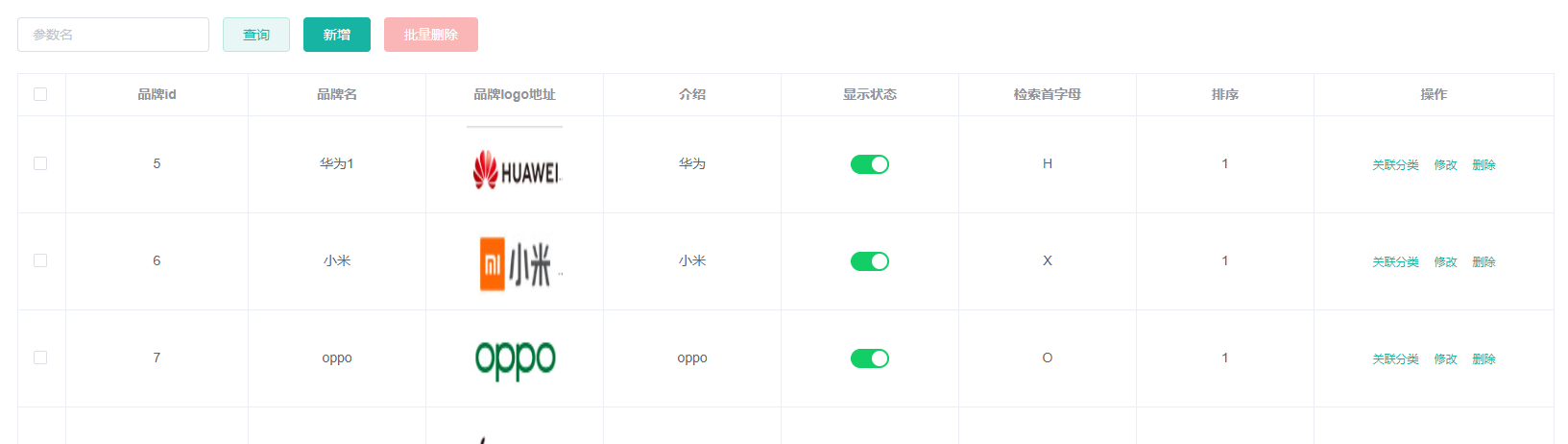
9.1、效果显示优化与快速显示开关

vue代码
<el-switch
v-model="scope.row.showStatus"
active-color="#13ce66"
inactive-color="#ff4949"
:active-value="1"
:inactive-value="0"
@change="updateBrandStatus(scope.row)"
>
<!--
scope.row 拿到整行的数据
active-color switch 打开时的背景色
inactive-color switch 关闭时的背景色
active-value switch 打开时的值
inactive-value switch 关闭时的值
-->组件地址:https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/switch
用户点击 switch 开关就会调用后台的接口更改对应数据库的字段 ( 决定是否显示),定义了 @change 事件 只要修后就会触发对应方法
updateBrandStatus(data) {
console.log("整行数据",data);
// 单独就封装两个字段
let {brandId,showStatus} = data
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl('/product/brand/update'),
method: 'post',
data: this.$http.adornData({brandId,showStatus}, false)
}).then(({ data }) => {
this.$message({
type:"success",
message:"状态更新成功"
})
});
},9.2、表单效验&自定义效验规则
Form 组件提供了表单验证的功能,只需要通过 rules 属性传入约定的验证规则,并将 Form-Item 的 prop 属性设置为需校验的字段名即可

<el-form
:model="dataForm"
:rules="dataRule"
ref="dataForm"
@keyup.enter.native="dataFormSubmit()"
label-width="140px"
>data中
自定义的规则 ,用来对数据进行判断
dataRule: {
name: [{ required: true, message: "品牌名不能为空", trigger: "blur" }],
// 自定义的规则
firstLetter: [
{ validator: (rule, value, callback) => {
if(value == '') {
callback(new Error("首字母必须填写"))
} else if(! /^[a-zA-Z]$/.test(value)) {
callback(new Error("首字母必须a-z或者A-Z之间"))
} else {
callback()
}
},trigger:'blur'}
],
sort: [{ validator: (rule, value, callback) => {
if(value == '') {
callback(new Error("排序字段必须填写"));
} else if(!Number.isInteger(value) || value < 0) {
callback(new Error("排序必须是一个大于等于0的整数"));
} else {
callback();
}
}, trigger: "blur" }]
}9.3、JSR303 数据效验 & 统一异常处理
前端数据效验成功了,就会把json数据传递到后端,但是有人利用接口 比如 postman 乱发送请求 那会怎么办,于是后端也会利用 JSR303进行数据效验
9.3.1、给Bean添加效验注解 javax.validation.constraints包下 并定义自己的的message提示

@NotEmpty(messsage = "logo不能为空")
@URL(message = "logo必须是一个合法的url地址")
private String logo;9.3.2、开启效验功能 @Valid
效果:效验错误以后有默认的响应
Controller代码:
@RequestMapping("/save") public R save(@Valid@RequestBody BrandEntity brand){ brandService.save(brand); return R.ok(); }
9.3.3、给效验的bean后紧跟一个BindingResult 就可以获取到效验的结果
public R save(@Valid @RequestBody BrandEntity brand,BindingResult result){
if(result.hasErrors()){
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
//1、获取校验的错误结果
result.getFieldErrors().forEach((item)->{
//FieldError 获取到错误提示
String message = item.getDefaultMessage();
//获取错误的属性的名字
String field = item.getField();
map.put(field,message);
});
return R.error(400,"提交的数据不合法").put("data",map);
}else {
}9.3.4、分组效验 (多场景复杂效验)
添加一个组 & 修改一个组
1、@NotBlank(message = "品牌名必须提交",groups = {AddGroup.class,UpdateGroup.class})
- 给效验注解标注什么情况需要进行效验
- @Validated({AddGroup.class}) 在对应方法上进行标注
- 默认没有指定分组的效验注解 @NotBlank 在分组效验情况@Validated({AddGroup.class})不生效,只会在@Validated生效
// 标记使用修改分组
public R update(@Validated(UpdateGroup.class) @RequestBody BrandEntity brand){
brandService.updateById(brand);
return R.ok();
}Entity
/**
* 品牌id
*/
@Null(message = "新增不能指定Id",groups = {AddGroup.class})
@NotNull(message = "修改必须指定品牌id",groups = {UpdateGroup.class})
@TableId
private Long brandId;
/**
* 品牌名
*/
@NotBlank(message = "品牌名不能为空",groups = {AddGroup.class,UpdateGroup.class})
private String name;
/**
* 品牌logo地址
*/
@NotEmpty(groups = {AddGroup.class})
@URL(message = "logo必须是一个合法的url地址",groups = {AddGroup.class,UpdateGroup.class})
private String logo;
/**
* 介绍
*/
private String descript;
/**
* 显示状态[0-不显示;1-显示]
*/
@NotNull(groups = {AddGroup.class, UpdateStatusGroup.class})
@ListValue(vals={0,1},groups = {AddGroup.class,UpdateStatusGroup.class})
private Integer showStatus;
/**
* 检索首字母
*/
@NotEmpty(groups = {AddGroup.class})
@Pattern(regexp = "^[a-zA-Z]$",message = "检索首字母必须是一个字母",groups = {AddGroup.class,UpdateGroup.class})
private String firstLetter;
/**
* 排序
*/
@NotNull(groups = {AddGroup.class})
@Min(value=0,message = "排序必须大于等于0",groups = {AddGroup.class,UpdateGroup.class})
private Integer sort;9.3.5、自定义效验
编写一个自定义的效验注解编写一个自定义的效验器何自定义的效验注解
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {ListValueConstraintValidator.class})//【可以指定多个不同的效验器,适配不同类型的效验】
@Target({ METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface ListValue {
// 三要素不能丢
String message() default "{com.atguigu.gulimall.product.valid.ListValue.message}";
Class<?>[] groups() default { };
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default { };
int[] vals() default { };
}实现约束
public class ListValueConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<ListValue,Integer> {
private Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
// 初始化方法
@Override
public void initialize(ListValue constraintAnnotation) {
int[] vals = constraintAnnotation.vals();
for(int val : vals) {
// 将结果添加到set集合
set.add(val);
}
}
/**
* 判断效验是否成功
* @param value 需要效验的值
* @param context
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid(Integer value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
// 判断是包含该值
return set.contains(value);
}
}9.3.6、异常处理
这里使用到了 SpringMVC 的注解 @ControllerAdvice
1、编写异常处理类使用SpringMvc的@ControllerAdvice
2、使用@ExceptionHandler标记方法可以处理异常
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.atguigu.gulimall.product.controller")
public class GulimallExceptionControllerAdvice {
/**
* 捕获定义的异常
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public R handleVaildException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error("数据效验出现问题{},异常类型:{}",e.getMessage(),e.getClass());
Map<String,String> errorMap = new HashMap<>();
BindingResult bindingResult = e.getBindingResult();
bindingResult.getFieldErrors().forEach(fieldError -> {
errorMap.put(fieldError.getField(),fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
});
return R.error(BizCodeEnume.VAILD_EXCEPTION.getCode(),BizCodeEnume.VAILD_EXCEPTION.getMsg()).put("data",errorMap);
}
/**
* 兜底异常
* @param throwable
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Throwable.class)
public R handleException(Throwable throwable) {
return R.error();
}
}异常错误码定义 (重点)
后端将定义的错误码写入到开发手册,前端出现对于的错误,就可以通过手册查询到对应的异常
/***
* 错误码和错误信息定义类
* 1. 错误码定义规则为5为数字
* 2. 前两位表示业务场景,最后三位表示错误码。例如:100001。10:通用 001:系统未知异常
* 3. 维护错误码后需要维护错误描述,将他们定义为枚举形式
* 错误码列表:
* 10: 通用
* 001:参数格式校验
* 11: 商品
* 12: 订单
* 13: 购物车
* 14: 物流
*
*
*/
public enum BizCodeEnume {
UNKNOW_EXCEPTION(10000,"系统未知异常"),
VAILD_EXCEPTION(10001,"参数格式校验失败");
private int code;
private String msg;
BizCodeEnume(int code,String msg){
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}十、商品服务&属性分组
10.1 、前端组件抽取 & 父子组件交互
10.1.1 属性分组 - 效果
左边这个树形空间我们已经写过了,在三级分类的时候编写过,相对应的功能,拖拽,添加,删除等等都已经实现,那我们为什么不把他抽取出一个公共的组件便于其他组件利用?
说干就干!
在 modules 中新建 common 文件夹,在common中 新建 category.vue
category.vue 核心代码
抽取需要的结果,多余的结果进行删除
<template>
<el-tree :data="menus" :props="defaultProps" node-key="catId" ref="menuTree" @node-click="nodeClick">
</el-tree>
</template>10.1.2 Layout 布局
通过基础的 24 分栏,迅速简便地创建布局、类似之前学过的bootstrap
<el-row :gutter="20">
<el-col :span="6">表格</el-col>
<el-col :span="18">菜单</el-col>
</el-row>左边放表格,右边放菜单
引入 category 组件
import category from "../common/category";并且声明
//import引入的组件需要注入到对象中才能使用
components: {
category
},最后在组件中使用
<el-col :span="6">
<!-- 直接使用-->
<category @tree-node-click="treenodeclick"></category>
</el-col>右边菜单使用代码生成器的代码直接引入即可
10.1.3 父子组件如何进行交互
子组件中的 Tree 组件的一个事件 node-click 节点被点击时的回调
// 向父组件发送事件,后面是需要传递的对象,参数等
this.$emit("tree-node-click",data,node,component)父组件需要定义相同方法接收
<category @tree-node-click="treenodeclick"></category> // 感知到节点被点击
treenodeclick(node, data, component) {
console.log("attrgroup感知到category节点被点击");
console.log("刚才被点击的菜单id:" + data.catId);
if (node.level == 3) {
this.catId = data.catId;
this.getDataList();
}
},10.2 、获取属性分类分组
查看提供的接口文档
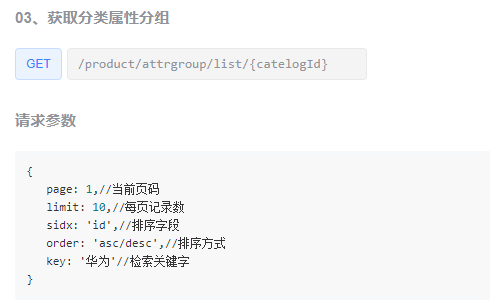
请求参数需要我们带对应的分页参数,所以我们在请求的时候得把参数带上
那就定义接口 go
/**
*
* @param params 分页请求相关参数
* @param catelogId 三级分类id
* @return
*/
PageUtils queryPage(Map<String, Object> params, Long catelogId);实现类
@Override
public PageUtils queryPage(Map<String, Object> params, Long catelogId) {
// 分类id 等于01 查询全部
if (catelogId == 0) {
IPage<AttrGroupEntity> page = this.page(new Query<AttrGroupEntity>().getPage(params),
new QueryWrapper<AttrGroupEntity>());
return new PageUtils(page);
} else {
// 拿到参数中的 key
String key = (String) params.get("key");
// 先根据分类id进行查询
QueryWrapper<AttrGroupEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<AttrGroupEntity>()
.eq("catelog_id",catelogId);
// selecet * from attrgroup where catelog_id = ? and (attr_group_id = key or like attr_group_name = key)
// 有时候查询也不会带上key 所以得判断
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
// where条件后加上 and
wrapper.and((obj) -> {
obj.eq("attr_group_id",key).or().like("attr_group_name",key);
});
}
// 组装条件进行查询
IPage<AttrGroupEntity> page = this.page(new Query<AttrGroupEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper);
return new PageUtils(page);
}
}10.3 、分类新增 & 级联选择器
级联选择器是啥?? 没接触过
官方解释
Cascader 级联选择器
当一个数据集合有清晰的层级结构时,可通过级联选择器逐级查看并选择。
对应效果
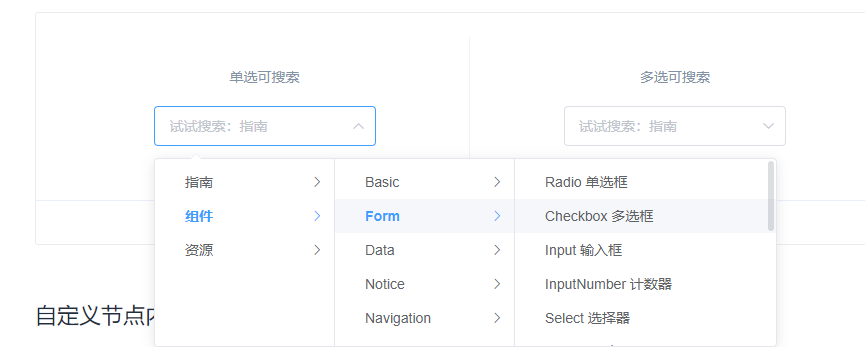
attrgroup-add-or-update.vue 中 加入该组件
<el-cascader
v-model="dataForm.catelogPath"
placeholder="试试搜索:手机"
:options="categorys"
:props="props"
filterable
></el-cascader>
<!--
placeholder="试试搜索:手机"默认的搜索提示
:options="categorys" 可选项数据源,键名可通过 Props 属性配置
:props="props" 配置选项
filterable 是否可搜索选项
-->那么问题来了? 我怎样把数据加载到这个组件里面?
在你组件加载完成后,我在调用方法 ( getCategorys() ) 获取菜单数据,在设置到options不就行了吗?
getCategorys(){
this.$http({
url: this.$http.adornUrl("/product/category/list/tree"),
method: "get"
}).then(({ data }) => {
this.categorys = data.data;
});
},10.4 、分类修改 & 回显级联选择器
修改和新增用的是一个添加组件 那么我们再点击修改后,你如何把 级联显示的数据再次显示出来?
在 AttrGroup点击修改后,会触发addOrUpdateHandle方法,他会通过引用 vue 文件里的 addOrUpdate 并调用他的 init初始化方法
// 新增 / 修改
addOrUpdateHandle(id) {
// 对话框显示
this.addOrUpdateVisible = true;
// 要渲染的组件完成选然后 调用该方法
this.$nextTick(() => {
// this 当前 refs 当前所有组件
this.$refs.addOrUpdate.init(id);
});
},init执行完成会回调
.then(({ data }) => {
if (data && data.code === 0) {
this.dataForm.attrGroupName = data.attrGroup.attrGroupName;
this.dataForm.sort = data.attrGroup.sort;
this.dataForm.descript = data.attrGroup.descript;
this.dataForm.icon = data.attrGroup.icon;
this.dataForm.catelogId = data.attrGroup.catelogId;
// 设置 级联的路径 从数据中取
this.dataForm.catelogPath = data.attrGroup.catelogPath;
}
});后端如何根据分组id 查询出 对应的分类?定义接口
/**
* 找到catelogId的完整路径
* 【父/子/孙】
* @param catelogId
*/
Long[] findCatelogPath(Long catelogId);实现
@Override
public Long[] findCatelogPath(Long catelogId) {
List<Long> paths = new ArrayList<>();
List<Long> parentPath = findParentPath(catelogId, paths);
// 反转
Collections.reverse(parentPath);
//转成Long[] 数组返回
return parentPath.toArray(new Long[parentPath.size()]);
}
/**
* 递归查找
* @param catelogId 三级分类的id
* @param paths 路径
* @return
*/
private List<Long> findParentPath(Long catelogId,List<Long> paths) {
// 1、收集当前节点id
paths.add(catelogId);
// 2、通过分类id拿到 Category 对象
CategoryEntity byId = this.getById(catelogId);
// 3、如果不是根节点 就一直递归下去查找
if (byId.getParentCid() != 0) {
findParentPath(byId.getParentCid(),paths);
}
return paths;
}在 AttrGroupEntity 中 添加了一个新属性
/**
* 用于存放 级联显示的 父子孙的地址
*/
@TableField(exist = false) // 标注为false 表是不是数据库字段
private Long[] catelogPath;Controller 具体设置返回数据
/**
* 信息
*/
@RequestMapping("/info/{attrGroupId}")
public R info(@PathVariable("attrGroupId") Long attrGroupId){
// 根据id查询出 分组group对象
AttrGroupEntity attrGroup = attrGroupService.getById(attrGroupId);
// 拿到分类id
Long catelogId = attrGroup.getCatelogId();
// 根据分类id查询出 他的 父 子 孙 对应的数据,并且设置到 attrGroup对象
Long[] catelogPath = categoryService.findCatelogPath(catelogId);
attrGroup.setCatelogPath(catelogPath);
return R.ok().put("attrGroup", attrGroup);
}10.5、品牌分类关联与级联更新
10.5.1、实现品牌管理搜索
在原本查询中加入新功能
@Override
public PageUtils queryPage(Map<String, Object> params) {
// 1、获取key
String key = (String) params.get("key");
QueryWrapper<BrandEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// key不为空 brand_id 和 name 进行值匹配
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.eq("brand_id",key).or().like("name",key);
}
IPage<BrandEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<BrandEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper
);
return new PageUtils(page);
}我们是直接把数据表存进了中间表,如果在真正的品牌名和分类名进行了修改,那么此时中间表的数据就是不对的,这时候数据就不是一致性
解决
在进行修改的时候,也要把中间表的数据进行更改
Brand
// BrandController
/**
/**
* 修改
*/
@RequestMapping("/update")
public R update(@Validated(UpdateGroup.class) @RequestBody BrandEntity brand){
brandService.updateDetail(brand);
return R.ok();
}
// Service
@Override
public void updateDetail(BrandEntity brand) {
// 保证字段一致
// 根据id更改
this.updateById(brand);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(brand.getName())) {
// 同步更新其他关联表中的数据
categoryBrandRelationService.updateBrand(brand.getBrandId(),brand.getName());
// TODO 更新其他关联
}
}
// Service实现类
@Override
public void updateBrand(Long brandId, String name) {
CategoryBrandRelationEntity relationEntity = new CategoryBrandRelationEntity();
relationEntity.setBrandName(name);
relationEntity.setBrandId(brandId);
this.update(relationEntity,new UpdateWrapper<CategoryBrandRelationEntity>().eq("brand_id",brandId));
}Category
@Override
public void updateCascate(CategoryEntity category) {
this.updateById(category);
categoryBrandRelationService.updateCategory(category.getCatId(),category.getName());
}
// Service
@Override
public void updateCascate(CategoryEntity category) {
// 更新自己表对象
this.updateById(category);
// 更新关联表对象
categoryBrandRelationService.updateCategory(category.getCatId(),category.getName());
}十一、商品服务&平台属性
11.1 规格参数新增与VO
11.1.1 获取分类规格参数
具体需求:
查询的数据没有分类和分组

属性分类 和 所属分组居然没有数据?
先查看返回的数据

发现没有 catelogName 和 AttrGroupName 的数据!! 原因是 AttrEntity没有这两个属性

但是他关联了 pms_attr_attrgroup_relation 表 这个表里面有 attr_Group_id 那么思路来了?
1、我先用 attr_id 去 pms_attr_attrgroup_relation中查询出 attr_Group_id 然后通过 attr_Group_id去pms_attr_group 表中查询出 分组的名称
2、自身 attr表中有 catelog_id 那我根据这个id去 category表中查询到 分类的姓名 不就行了吗?
上代码
@Override
public PageUtils queryBaseAttrPage(Map<String, Object> params, Long catelogId) {
QueryWrapper<AttrEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
if (catelogId != 0) {
wrapper.eq("catelog_id",catelogId);
}
String key = (String) params.get("key");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.and((wrapper1) -> {
wrapper1.eq("attr_id",key).or().like("attr_name",key);
});
}
IPage<AttrEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<AttrEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper
);
PageUtils pageUtils = new PageUtils(page);
// 拿到分页记录
List<AttrEntity> records = page.getRecords();
List<AttrRespVo> respVo = records.stream().map((attrEntity) -> {
AttrRespVo attrRespVo = new AttrRespVo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(attrEntity, attrRespVo);
// 1、设置分类和分组的名字
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity attr_idEntity = relationDao.selectOne(new QueryWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>()
.eq("attr_id", attrEntity.getAttrId()));
if (attr_idEntity != null) {
AttrGroupEntity attrGroupEntity = attrGroupDao.selectById(attr_idEntity.getAttrGroupId());
attrRespVo.setGroupName(attrGroupEntity.getAttrGroupName());
}
CategoryEntity categoryEntity = categoryDao.selectById(attrEntity.getCatelogId());
if (categoryEntity != null) {
attrRespVo.setCatelogName(categoryEntity.getName());
}
return attrRespVo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
pageUtils.setList(respVo);
return pageUtils;
}但是原先的 AttrEntity 对象里面任然没有这两个属性 ! 怎么解决
1、我直接在 AttrEntity中新建对应的字段不就行了吗? 然后设置成不是数据库的字段
缺点:这样子是不是太乱了?
2、新建一个 VO 抽取出这两个属性 不就行了吗?
@Data
public class AttrRespVo extends AttrVo {
/**
* catelogName 手机数码,所属分类名字
* groupName 主体 所属分组名字
*/
private String catelogName;
private String groupName;
}11.2 规格参数列表&规格修改
11.2.1、获取分类规格参数
/**
* 获取分类规格参数
attrType 和 catelogId 通用
* @param params
* @param catelogId
* @param type sale 销售属性 base 规格参数
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{attrType}/list/{catelogId}")
public R baseAttrList(@RequestParam Map<String,Object> params
,@PathVariable("catelogId") Long catelogId,
@PathVariable("attrType") String type) {
PageUtils page = attrService.queryBaseAttrPage(params,catelogId,type);
return R.ok().put("page",page);
}实现类
@Override
public PageUtils queryBaseAttrPage(Map<String, Object> params, Long catelogId, String type) {
// 先根据 attr_type字段进行查询 该字段表示 1是基本属性 0是销售属性,基本属性和销售属性我们放在一张表内
QueryWrapper<AttrEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<AttrEntity>()
.eq("attr_type","base".equalsIgnoreCase(type)?
ProductConstant.AttrEnum.ATTR_TYPE_BASE.getCode():
ProductConstant.AttrEnum.ATTR_TYPE_SALE.getCode());
// 分类id不等于0 按照分类id进行查询
if (catelogId != 0) {
wrapper.eq("catelog_id",catelogId);
}
// 取出参数 key,进行条件查询
String key = (String) params.get("key");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.and((wrapper1) -> {
wrapper1.eq("attr_id",key).or().like("attr_name",key);
});
}
// 封装分页数据
IPage<AttrEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<AttrEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper
);
PageUtils pageUtils = new PageUtils(page);
// 拿到全部的分页记录
List<AttrEntity> records = page.getRecords();
// 查询所属分类以及所属分组
List<AttrRespVo> respVo = records.stream().map((attrEntity) -> {
// 实例化数据传输对象 将 attrEntity的分类名字以及分组名字 复制到该对象
AttrRespVo attrRespVo = new AttrRespVo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(attrEntity, attrRespVo);
// Controller地址如果是 基础 才进行查询分裂
if("base".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
// 1、根据attr_id 查询到 attr和 attrGroup的关系表
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity attr_idEntity = relationDao.selectOne(new QueryWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>()
.eq("attr_id", attrEntity.getAttrId()));
//查询到的关系对象以及分组id不为空
if (attr_idEntity != null && attr_idEntity.getAttrGroupId()!=null) {
// 根据分组id查询到分组信息
AttrGroupEntity attrGroupEntity = attrGroupDao.selectById(attr_idEntity.getAttrGroupId());
attrRespVo.setGroupName(attrGroupEntity.getAttrGroupName());
}
}
// 根据attrEntity的分类id 查询到分类对象并设置分类姓名
CategoryEntity categoryEntity = categoryDao.selectById(attrEntity.getCatelogId());
if (categoryEntity != null) {
attrRespVo.setCatelogName(categoryEntity.getName());
}
return attrRespVo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//封装到分页工具类
pageUtils.setList(respVo);
return pageUtils;
}先是根据 catelog_id查询到AttrEntity 对象 该对象里拥有 attr_id 然后根据attr_id 去 pms_attr_attrgroup_relation表进行查询
11.2.2、查询属性详情

Controller
/**
* 信息
*/
@RequestMapping("/info/{attrId}")
public R info(@PathVariable("attrId") Long attrId){
AttrRespVo attr = attrService.getAttrInfo(attrId);
return R.ok().put("attr", attr);
}Service 实现
@Override
public AttrRespVo getAttrInfo(Long attrId) {
// 实例化封装VO数据对象
AttrRespVo attrRespVo = new AttrRespVo();
// 根据attrid查询出商品属性
AttrEntity attrEntity = this.getById(attrId);
// 将商品属性对象的属性复制到 VO数据对象
BeanUtils.copyProperties(attrEntity, attrRespVo);
// attrType == 1为基本类型才进行查询分组信息
if (attrEntity.getAttrType() == ProductConstant.AttrEnum.ATTR_TYPE_BASE.getCode()) {
// 根据 attr_id 查询到 商品属性以及商品分组关系表
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity relationEntity = relationDao.selectOne(new QueryWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>()
.eq("attr_id", attrId));
if (relationEntity != null) {
// 设置分组id
attrRespVo.setAttrGroupId(relationEntity.getAttrGroupId());
// 分组&商品信息关系表拿到分组id 查询到分组对象
AttrGroupEntity attrGroupEntity = attrGroupDao.selectById(relationEntity.getAttrGroupId());
if (attrGroupEntity != null) {
//不为空设置分组姓名
attrRespVo.setGroupName(attrGroupEntity.getAttrGroupName());
}
}
}
// 从当前商品属性对象中拿到分类id进行设置分类信息
Long catelogId = attrEntity.getCatelogId();
// 根据 catelogId 查询到分类 父 子 孙 路径
Long[] catelogPath = categoryService.findCatelogPath(catelogId);
attrRespVo.setCatelogPath(catelogPath);
//最后根据分类id 查询到分类对象 并进行设置分类姓名
CategoryEntity categoryEntity = categoryService.getById(catelogId);
if (categoryEntity != null) {
attrRespVo.setCatelogName(categoryEntity.getName());
}
return attrRespVo;
}主要理解: 先是根据 attrId 查询到商品属性 然后根据 attrId 查询到分类关系表 该表中有分组id attrGroup_id 通过这个查询到 分组对象信息,
,同时在 商品属性表中拿到 分类id 通过分类id 查询到 查询到分类对象 同时根据 分类id查询对应层级关系,并设置分类姓名
11.3.3、销售属性

销售属性 和 基本属性 通过一个字段来区分,对应的修改,查询 都用的同一个方法,所以在方法的中 也进行了对应的判断
保存
@Override
public void saveAttr(AttrVo attr) {
AttrEntity attrEntity = new AttrEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(attr, attrEntity);
// 保存基本数据
this.save(attrEntity);
// 2、保存关联关系
// 等于1 说明基本属性 才进行保存分组关系
if (attr.getAttrType() == ProductConstant.AttrEnum.ATTR_TYPE_BASE.getCode() && attr.getAttrGroupId() != null) {
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity relationEntity = new AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity();
relationEntity.setAttrGroupId(attr.getAttrGroupId());
relationEntity.setAttrId(attrEntity.getAttrId());
relationDao.insert(relationEntity);
}
}修改
@Transactional
@Override
public void updateAttr(AttrVo attr) {
// Vo数据传输对象属性拷贝到 attrEntity对象
AttrEntity attrEntity = new AttrEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(attr, attrEntity);
this.updateById(attrEntity);
// attrType 等于 1 也就是基本属性
if (attrEntity.getAttrType() == ProductConstant.AttrEnum.ATTR_TYPE_BASE.getCode()) {
//1、修改分组关联
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity relationEntity = new AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity();
// 设置attrid 以及 分组id
relationEntity.setAttrId(attr.getAttrId());
relationEntity.setAttrGroupId(attr.getAttrGroupId());
// 关系表中根据attr_id 进行更新
relationDao.update(relationEntity, new UpdateWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>().
eq("attr_id", attr.getAttrId()));
// 根据 attr_id 是否可以查询到结果
Integer count = relationDao.selectCount(new QueryWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>().
eq("attr_id", attr.getAttrId()));
// 查得到
if (count > 0) {
// 进行更新
relationDao.update(relationEntity, new UpdateWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>().
eq("attr_id", attr.getAttrId()));
} else {
// 查不到意味着 没有该记录 则进行插入
relationDao.insert(relationEntity);
}
}
}11.3 查询分类关联属性&删除关联&查询分组未关联属性
11.3.1、获取属性分组的关联的所有属性
/**
* 获取属性分组的关联的所有属性
* @param attrgroupId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{attrgroupId}/attr/relation")
public R attrRelation(@PathVariable("attrgroupId") Long attrgroupId) {
List<AttrEntity> entityList = attrService.getRelationAttr(attrgroupId);
return R.ok().put("data", entityList);
}Service 实现
/**
* 根据分组id查找关联的所有基本属性
* @param attrgroupId
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<AttrEntity> getRelationAttr(Long attrgroupId) {
// 根据attr_group_id 查询到 关系表
List<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity> entities = relationDao.selectList(new QueryWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>()
.eq("attr_group_id", attrgroupId));
// 从关系表中 取到 属性id
List<Long> attrIds = entities.stream().map((attr) -> {
return attr.getAttrId();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (attrIds == null || attrIds.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
// 按照属性id进行查询
Collection<AttrEntity> attrEntities = this.listByIds(attrIds);
return (List<AttrEntity>) attrEntities;
}
已知有参数 attr_group_id 进行查询 能查到 attr_id,在利用 attr_id 查询到 attr相关信息
11.3.2、删除属性与分组的关联关系

/**
* 删除属性与分组的关联关系
* @param relationVo
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/attr/relation/delete")
public R deleteRelation(@RequestBody AttrGroupRelationVo[] relationVo) {
attrService.deleteRelation(relationVo);
return R.ok();
}Service 实现
@Override
public void deleteRelation(AttrGroupRelationVo[] relationVo) {
// 转成 list 进行stream流处理
List<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity> entities = Arrays.asList(relationVo).stream().map((item) -> {
// 将 item对应属性拷贝到 relationEntity对象中
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity relationEntity = new AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, relationEntity);
return relationEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// id批量删除
relationDao.deleteBatchRelation(entities);
}deleteBatchRelation 方法
<delete id="deleteBatchRelation">
DELETE FROM `pms_attr_attrgroup_relation` WHERE
<!- 循环遍历进行删除 使用的是 or-->
<foreach collection="entities" item="item" separator=" OR ">
( attr_id=#{item.attrId} AND attr_group_id=#{item.attrGroupId} )
</foreach>
</delete>11.3.3、查询分组未关联属性
@GetMapping("/{attrgroupId}/noattr/relation")
public R attrNoRelation(@PathVariable("attrgroupId") Long attrgroupId,
@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params) {
PageUtils page = attrService.getNoRelationAttr(params,attrgroupId);
return R.ok().put("page",page);
}Service
@Override
public PageUtils getNoRelationAttr(Map<String, Object> params, Long attrgroupId) {
// 1、当前分组只能关联自己所属分类里面的所有属性
AttrGroupEntity attrGroupEntity = attrGroupDao.selectById(attrgroupId);
Long catelogId = attrGroupEntity.getCatelogId();
//2、当前分组只能关联别的分组没有引用的属性
//2.1 当前分类下的 **其他分组** 根据分类id进行查询
List<AttrGroupEntity> group = attrGroupDao.selectList(new QueryWrapper<AttrGroupEntity>()
.eq("catelog_id", catelogId));
// 拿到分组id
List<Long> collect = group.stream().map(item -> {
return item.getAttrGroupId();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//2.2 这些分组关联的属性 根据分组id查询出关联表
List<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity> groupId = relationDao.selectList(new QueryWrapper<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity>()
.in("attr_group_id", collect));
// 拿到所有的属性id
List<Long> attrIds = groupId.stream().map((item) -> {
return item.getAttrId();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//2.3 从当前分类的所有属性中移除这些属性
QueryWrapper<AttrEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<AttrEntity>()
.eq("catelog_id", catelogId)
.eq("attr_type", ProductConstant.AttrEnum.ATTR_TYPE_BASE.getCode());
// attrIds 属性id数组不为空
if (attrIds != null && attrIds.size() > 0) {
// 在attrids 数组中得id不用进行查询
wrapper.notIn("attr_id", attrIds);
}
//取出参数进行 对应条件查询
String key = (String) params.get("key");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.and((w) -> {
w.eq("attr_id", key).or().like("attr_name", key);
});
}
// 根据分页数据 以及 wrapper进行查询
IPage<AttrEntity> page = this.page(new Query<AttrEntity>().getPage(params), wrapper);
PageUtils pageUtils = new PageUtils(page);
return pageUtils;
}11.4.4、新增分组与属性关联
@PostMapping("/attr/relation")
public R addRelation(@RequestBody List<AttrGroupRelationVo> attrGroupRelationVo) {
attrAttrgroupRelationService.saveBatch(attrGroupRelationVo);
return R.ok();
}Service
@Override
public void saveBatch(List<AttrGroupRelationVo> attrGroupRelationVo) {
List<AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity> collect = attrGroupRelationVo.stream().map((item) -> {
// 复制属性 返回
AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity relationEntity = new AttrAttrgroupRelationEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, relationEntity);
return relationEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
this.saveBatch(collect);
}业务之间需要多种测试 各种判断
十二、商品服务&新增商品
12.1 获取分类关联的品牌

前端发送请求

后端编写:
Controller
/**
* 获取分类关联的品牌
* @param catId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/brands/list")
public R relationBrandList(@RequestParam(value = "catId",required = true) Long catId) {
List<BrandEntity> vos = categoryBrandRelationService.getBrandCatId(catId);
//拿到 品牌对象数据后 从中抽取除 品牌姓名和id
List<BrandVo> collect = vos.stream().map(item -> {
BrandVo brandVo = new BrandVo();
brandVo.setBrandId(item.getBrandId());
brandVo.setBrandName(item.getName());
return brandVo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return R.ok().put("data",collect);
}Service实现
@Override
public List<BrandEntity> getBrandCatId(Long catId) {
// 根据分类id查询出 分类和品牌的关系表
List<CategoryBrandRelationEntity> catelogId = categoryBrandRelationDao.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryBrandRelationEntity>().eq("catelog_id", catId));
List<BrandEntity> collect = catelogId.stream().map(item -> {
//根据品牌id查询出品牌对象
BrandEntity brandEntity = brandDao.selectById(item.getBrandId());
return brandEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect;
}总结:
业务操作设计两个表
- pms_brand
- pms_category_brand_relation
请求参数是 CatId Long类型
- 先根据 CatId 在 pms_category_brand_relation表中查询到品牌 Id
- 拿到 brand_id 查询出 brand 的相关信息
- 组装成 BrandVo 后 返回

12.2 获取分类下所有分组以及属性

基本信息输入成功后,就会跳转到规格参数,
并根据分类id查询出对应数据

Controller
/**
* 获取分类下所有分组&关联属性
* @param catelogId
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/{catelogId}/withattr")
public R getAttrGroupWithAttrs(@PathVariable("catelogId") Long catelogId) {
List<AttrGroupWithAttrsVo> vos = attrGroupService.getAttrGroupWithAttrsByCatelogId(catelogId);
return R.ok().put("data",vos);
}Service 实现
@Override
public List<AttrGroupWithAttrsVo> getAttrGroupWithAttrsByCatelogId(Long catelogId) {
// 1、根据分类id查询出 查询分组关系
List<AttrGroupEntity> attrgroupEntites = this.list(new QueryWrapper<AttrGroupEntity>().eq("catelog_id", catelogId));
List<AttrGroupWithAttrsVo> collect = attrgroupEntites.stream().map(group -> {
AttrGroupWithAttrsVo attrsVo = new AttrGroupWithAttrsVo();
// 2、将分组属性拷贝到 VO中
BeanUtils.copyProperties(group, attrsVo);
// 3、通过分组id查询出 商品属性信息
// 调用 getRelationAttr方法先根据 分组id去 中间关系表查询到商品属性id 然后根据商品属性id查询到商品信息
List<AttrEntity> relationAttr = attrService.getRelationAttr(attrsVo.getAttrGroupId());
attrsVo.setAttrs(relationAttr);
return attrsVo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return collect;
}12.3 商品 VO 抽取&商品新增业务流程
商品属性、销售属性、规格参数、基本信息都填好了后就会生成一串 JSON

我们将 json 放到 json解析网站上 并生成对应得实体类

12.3.4 封装 Vo 中,更改对应得属性

有些参与计算的属性 如 int price 将类型更改为 BigDecimal
12.3.5 分析业务流程
业务流程:

12.3.6 主要编码!
@Transactional
@Override
public void saveSpuInfo(SpuSaveVo vo) {
// 1、保存Spu基本信息 pms_spu_info
SpuInfoEntity spuInfoEntity = new SpuInfoEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(vo,spuInfoEntity);
spuInfoEntity.setCreateTime(new Date());
spuInfoEntity.setUpdateTime(new Date());
this.saveBaseSpuInfo(spuInfoEntity);
// 2、保存Spu的描述信息 pms_spu_info_desc
List<String> decript = vo.getDecript();
SpuInfoDescEntity spuInfoDescEntity = new SpuInfoDescEntity();
// SpuInfoEntity保存到取得 spuId 设置到 Desc中
spuInfoDescEntity.setSpuId(spuInfoEntity.getId());
// 以逗号来拆分
spuInfoDescEntity.setDecript(String.join(",",decript));
spuInfoDescService.saveSpuInfoDesc(spuInfoDescEntity);
// 3、保存Spu的图片集 pms_spu_images
List<String> imageList = vo.getImages();
spuImagesService.saveImages(spuInfoEntity.getId(),imageList);
// 4、保存spu的规格参数 pms_product_attr_value
List<BaseAttrs> baseAttrs = vo.getBaseAttrs();
List<ProductAttrValueEntity> collect = baseAttrs.stream().map(attr -> {
// 设置 spu 属性值
ProductAttrValueEntity valueEntity = new ProductAttrValueEntity();
valueEntity.setAttrId(attr.getAttrId());
AttrEntity attrEntity = attrService.getById(attr.getAttrId());
valueEntity.setAttrName(attrEntity.getAttrName());
valueEntity.setSpuId(spuInfoEntity.getId());
valueEntity.setQuickShow(attr.getShowDesc());
valueEntity.setAttrValue(attr.getAttrValues());
return valueEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
attrValueService.saveProductAttr(collect);
// 5、保存SPU的积分信息 gulimall_sms sms => sms_spu_bounds
Bounds bounds = vo.getBounds();
SpuBoundTo spuBoundTo = new SpuBoundTo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(bounds,spuBoundTo);
spuBoundTo.setSpuId(spuInfoEntity.getId());
// 远程服务调用
R r = couponFeignService.saveSpuBounds(spuBoundTo);
if (r.getCode() != 0) {
log.error("远程保存优惠信息失败");
}
// 5、保存当前Spu对应的所有SKU信息
List<Skus> skus = vo.getSkus();
if (skus != null && skus.size() > 0) {
// 遍历 skus 集合
skus.forEach(item ->{
String defaultImage = "";
// 遍历 skus 集合中的图片
for (Images image : item.getImages()) {
// 默认图片等于 1 该记录则是默认图片
if (image.getDefaultImg() == 1) {
defaultImage = image.getImgUrl();
}
}
// private String skuName;
// private String price;
// private String skuTitle;
// private String skuSubtitle;
// 只有上面4个属性相同
SkuInfoEntity skuInfoEntity = new SkuInfoEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,skuInfoEntity);
// 其他属性需要自己赋值
skuInfoEntity.setBrandId(spuInfoEntity.getBrandId());
skuInfoEntity.setCatalogId(spuInfoEntity.getCatalogId());
skuInfoEntity.setSaleCount(0L);
skuInfoEntity.setSpuId(spuInfoDescEntity.getSpuId());
skuInfoEntity.setSkuDefaultImg(defaultImage);
//5.1、SKU的基本信息 pms_sku_info
skuInfoService.saveSkuInfo(skuInfoEntity);
Long skuId = skuInfoEntity.getSkuId();
// 保存 sku 图片信息
List<SkuImagesEntity> imagesEntities = item.getImages().stream().map(img -> {
SkuImagesEntity skuImagesEntity = new SkuImagesEntity();
skuImagesEntity.setSkuId(skuId);
skuImagesEntity.setImgUrl(img.getImgUrl());
skuImagesEntity.setDefaultImg(img.getDefaultImg());
return skuImagesEntity;
}).filter(entity ->{
//返回 true 需要 false 过滤
return !StringUtils.isEmpty(entity.getImgUrl());
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// TODO 没有图片路径的无需保存
//5.2、SKU的图片信息 pms_sku_images
skuImagesService.saveBatch(imagesEntities);
List<Attr> attr = item.getAttr();
// 保存 sku 销售属性
List<SkuSaleAttrValueEntity> skuSaleAttrValueEntities = attr.stream().map(a -> {
SkuSaleAttrValueEntity skuSaleAttrValueEntity = new SkuSaleAttrValueEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(a, skuSaleAttrValueEntity);
skuSaleAttrValueEntity.setSkuId(skuId);
return skuSaleAttrValueEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//5.3、SKU的销售属性信息 pms_sku_sale_attr_value
saleAttrValueService.saveBatch(skuSaleAttrValueEntities);
//5.4、SKU的优惠、满减等信息 gulimall_sms ->sms_sku_ladder \sms_sku_full_reduction\sms_member_price
SkuReductionTo skuReductionTo = new SkuReductionTo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,skuReductionTo);
skuReductionTo.setSkuId(skuId);
if (skuReductionTo.getFullCount() > 0 || skuReductionTo.getFullPrice().compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1) {
R r1 = couponFeignService.saveSkuReduction(skuReductionTo);
if (r1.getCode() != 0) {
log.error("远程保存sku优惠信息失败");
}
}
});
}
}saveImages
@Override
public void saveImages(Long id, List<String> imageList) {
if (imageList == null || imageList.size() <=0) {
log.error("图片为空!!!!!!");
} else {
List<SpuImagesEntity> collect = imageList.stream().map(img -> {
SpuImagesEntity entity = new SpuImagesEntity();
// 设置主要属性
entity.setSpuId(id);
entity.setImgUrl(img);
return entity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
this.saveBatch(collect );
}
}远程服务调用 对应方法
保存了 商品阶梯价格、商品满减信息、商品会员价格
@Override
public void saveSkuReduction(SkuReductionTo skuReductionTo) {
//5.4、SKU的优惠、满减等信息 gulimall_sms ->sms_sku_ladder \sms_sku_full_reduction\sms_member_price
//sms_sku_ladder
SkuLadderEntity skuLadderEntity = new SkuLadderEntity();
skuLadderEntity.setSkuId(skuReductionTo.getSkuId());
skuLadderEntity.setFullCount(skuReductionTo.getFullCount());
skuLadderEntity.setAddOther(skuReductionTo.getCountStatus());
skuLadderEntity.setDiscount(skuReductionTo.getDiscount());
if (skuLadderEntity.getFullCount() > 0) {
skuLadderService.save(skuLadderEntity);
}
//sms_sku_full_reduction
SkuFullReductionEntity skuFullReductionEntity = new SkuFullReductionEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(skuReductionTo,skuFullReductionEntity);
// BigDecimal 用 compareTo来比较
if (skuFullReductionEntity.getFullPrice().compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1) {
this.save(skuFullReductionEntity);
}
//sms_member_price
List<MemberPrice> memberPrice = skuReductionTo.getMemberPrice();
List<MemberPriceEntity> collect = memberPrice.stream().map(item -> {
MemberPriceEntity priceEntity = new MemberPriceEntity();
priceEntity.setSkuId(skuReductionTo.getSkuId());
priceEntity.setMemberPrice(item.getPrice());
priceEntity.setMemberLevelName(item.getName());
priceEntity.setMemberLevelId(item.getId());
priceEntity.setAddOther(1);
return priceEntity;
}).filter(item -> {
// 会员对应价格等于0 过滤掉
return item.getMemberPrice().compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
memberPriceService.saveBatch(collect);
}12.3.7 总结
- 电商系统中大表数据不做关联 宁可一点一点查询
- 商品新增业务,眨眼一看很多代码,但是如果把他们划分成几个功能点一一完成,业务也就不会变得很庞大
相关操作的表

12.3.8 商品保存后 Debug 调试
很少有一次写的代码能一次通过,所以我们要 一个功能点一个断点来调试程序是否正确
# 将当前会话等级设置成读为提交,当前窗口就能查看到没有提交的数据
SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED;具体 Debug 过程不在此叙述
12.3.9 商品保存其他问题处理
1、 sku_images 表中 img_url 字段为空
sku_images 中有很多图片都是为空,因此我们需要在程序中处理这个数据,空数据不写入到数据库中

解决思路:
skuImages 保存部分代码、如果 ImgUrl 为空则进行过滤
}).filter(entity ->{
//返回 true 需要 false 过滤
return !StringUtils.isEmpty(entity.getImgUrl());
}).collect(Collectors.toList());2、sku 满减以及打折信息 数据出现错误
有部分数据 为0

解决思路:
在代码中过滤对应为0的数据
部分修改代码
// 满几件 大于0 可以添加 满多少钱 至少要大于0
if (skuReductionTo.getFullCount() > 0 || skuReductionTo.getFullPrice().compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1) {
R r1 = couponFeignService.saveSkuReduction(skuReductionTo);
if (r1.getCode() != 0) {
log.error("远程保存sku优惠信息失败");
}
}远程服务中也进行对应修改
/**
保存 商品阶梯价格
件数 大于0才能进行修改
**/
if (skuLadderEntity.getFullCount() > 0) {
skuLadderService.save(skuLadderEntity);
}
/**
保存商品满减信息
**/
// BigDecimal 用 compareTo来比较
if (skuFullReductionEntity.getFullPrice().compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1) {
this.save(skuFullReductionEntity);
}
/**
保存商品会员价格
也进行了过滤数据
**/
}).filter(item -> {
// 会员对应价格等于0 过滤掉
return item.getMemberPrice().compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());3、程序中其他的异常
程序中总会出现一些其他的异常的,这个留到高级篇进行讲解
十三、 商品服务&商品管理
13.1 商品管理 SPU 检索
功能概述:
- 查询刚刚发布的商品,并能进行对应的条件查询

Controller
/**
* 列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
//@RequiresPermissions("product:spuinfo:list")
public R list(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params){
PageUtils page = spuInfoService.queryPageByCondition(params);
return R.ok().put("page", page);
}Service 实现
/**
* 根据条件进行查询 spu相关信息
* @param params 分页参数 status上架状态,catelogId 分类id brandId 品牌id
* @return
*/
@Override
public PageUtils queryPageByCondition(Map<String, Object> params) {
QueryWrapper<SpuInfoEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 取出参数 key 进行查询
String key = (String) params.get("key");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.and((w) ->{
w.eq("id","key").or().like("spu_name",key);
});
}
// 验证不为空 取出参数进行 查询
String status = (String) params.get("status");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(status)) {
wrapper.eq("publish_status",status);
}
String brandId = (String) params.get("brandId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(brandId) && ! "0".equalsIgnoreCase(brandId)) {
wrapper.eq("brand_id",brandId);
}
String catelogId = (String) params.get("catelogId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(catelogId) && ! "0".equalsIgnoreCase(catelogId)) {
wrapper.eq("catalog_id",catelogId);
}
IPage<SpuInfoEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<SpuInfoEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper);
return new PageUtils(page);
}总结业务流程
- 主要查询的是
pms_spu_info这张表 前端传递过来的参数 主要有分页,以及 品牌id 分类id 我们需要判断这些值是否正确,然后进行查询数据
13.1 商品管理 SkU 检索
功能概述:
查询具体的商品管理 库存

Controller
/**
* 列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
//@RequiresPermissions("product:skuinfo:list")
public R list(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params){
PageUtils page = skuInfoService.queryPageByCondition(params);
return R.ok().put("page", page);
}Service
@Override
public PageUtils queryPageByCondition(Map<String, Object> params) {
QueryWrapper<SkuInfoEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 取出参数 进行查询
String key = (String) params.get("key");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.and((w) ->{
w.eq("sku_id",key).or().like("sku_name",key);
});
}
// 验证 id 是否为0 否则进行匹配
String catelogId = (String) params.get("catelogId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(catelogId) && !"0".equalsIgnoreCase(catelogId)) {
wrapper.eq("catalog_id",catelogId);
}
String brandId = (String) params.get("brandId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(brandId) && !"0".equalsIgnoreCase(brandId)) {
wrapper.eq("brand_id",brandId);
}
String min = (String) params.get("min");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(min)) {
wrapper.ge("price",min);
}
String max = (String) params.get("max");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(max) ) {
// 怕前端传递的数据是 abc 等等 所以要抛出异常
try {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal(max);
if ( bigDecimal.compareTo(new BigDecimal("0")) == 1) {
wrapper.le("price",max);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
IPage<SkuInfoEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<SkuInfoEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper
);
return new PageUtils(page);
}总结业务流程:
主要查询是 pms_sku_info 这张表,我出现的问题是发布商品时候,实体类的 价格 与 VO属性不一致,出现了数据没有拷贝,修改后,数据查询正常
十四、仓储服务&仓库管理
14.1 整合ware服务&获取仓库列表
14.1.1整合 ware 服务
1、首先服务需要先注册到 Nacos 中,需要自己配置文件 配置对应的 nacos注册地址,
2、启动类需要开启 服务注册发现,开启远程服务调用
@EnableFeignClients // 开启openfeign 远程服务调用
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.gulimall.ware.dao") //mapper包扫描
@EnableDiscoveryClient //服务注册发现14.1.2 获取仓库列表
具体需求:
根据参数名查询出 仓库相关的记录 ,具体对于操作的是wms_ware_info 表

Controller
/**
* 列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
//@RequiresPermissions("ware:wareinfo:list")
public R list(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params){
PageUtils page = wareInfoService.queryPage(params);
return R.ok().put("page", page);
}Service
@Override
public PageUtils queryPage(Map<String, Object> params) {
QueryWrapper<WareInfoEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 取出参数
String key = (String)params.get("key");
// 拼接条件
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.eq("id",key).or()
.like("name",key)
.eq("address",key)
.eq("areacode",key);
}
IPage<WareInfoEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<WareInfoEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper
);
return new PageUtils(page);
}总结业务流程
仓库维护对应的是 wms_ware_info 根据前端传递过来的参数进行拼接然后进行查询
14.2 查询库存&创建采购需求
14.2.1 查询库存
具体需求:
根据 仓库、skuId 进行查询对应的表是 wms_ware_sku

Controller
/**
* 列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
//@RequiresPermissions("ware:waresku:list")
public R list(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params){
PageUtils page = wareSkuService.queryPage(params);
return R.ok().put("page", page);
}Service
@Override
public PageUtils queryPage(Map<String, Object> params) {
QueryWrapper<WareSkuEntity> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 取出请求的参数 组装条件进行查询
String skuId = (String) params.get("skuId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(skuId)) {
queryWrapper.eq("sku_id",skuId);
}
String wareId = (String) params.get("wareId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(wareId)) {
queryWrapper.eq("ware_id",wareId);
}
IPage<WareSkuEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<WareSkuEntity>().getPage(params),
queryWrapper
);
return new PageUtils(page);
}总结业务流程:
wms_ware_sku 主要的操作的就是该表 一样的封装条件,然后进行查询
14.2.2 创建采购需求
具体需求:
选择 仓库、状态、 以及其他关键字 查询出对应的数据 那么查询的是哪张表? wms_purchase_detail

Controller
如往常一样 调用 Service 返回结果 组装 返回~~~
/**
* 列表
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
//@RequiresPermissions("ware:purchasedetail:list")
public R list(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params){
PageUtils page = purchaseDetailService.queryPage(params);
return R.ok().put("page", page);
}Service
/**
* // status: 0,//状态
* // wareId: 1,//仓库id
* @param params
* @return
*/
@Override
public PageUtils queryPage(Map<String, Object> params) {
QueryWrapper<PurchaseDetailEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
// 取出key
String key = (String) params.get("key");
// key 主要查询条件
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
wrapper.and((w) ->{
w.eq("purchase_id",key).or().eq("sku_id",key);
});
}
String status = (String) params.get("status");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(status)) {
wrapper.and((w) ->{
w.eq("status",status);
});
}
String wareId = (String) params.get("wareId");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(wareId)) {
wrapper.and((w) ->{
w.eq("ware_id",wareId);
});
}
IPage<PurchaseDetailEntity> page = this.page(
new Query<PurchaseDetailEntity>().getPage(params),
wrapper
);
return new PageUtils(page);
}总结业务流程:
对 wms_purchase_detail 表进行操作 拼装条件 查询 嗯 就这样~~~
14.3 合并采购需求&领取采购单&完成采购&Spu规格维护
14.3.1 合并采购需求
具体需求:

选中 点击批量操作

请求参数分享
{
purchaseId: 1, //整单id
items:[1,2,3,4] //合并项集合
}那就建立对应的 Vo 用来接收请求参数
Controller
/**
* 合并采购
* @param mergeVo
* @return
*/
///ware/purchase/merge
@PostMapping("/merge")
public R merge(@RequestBody MergeVo mergeVo) {
purchaseService.mrgePurchase(mergeVo);
return R.ok();
}Service
/**
* 合并采购需求
* @param mergeVo
*/
@Transactional
@Override
public void mrgePurchase(MergeVo mergeVo) {
// 拿到采购单id
Long purchaseId = mergeVo.getPurchaseId();
// 采购单 id为空 新建
if (purchaseId == null ) {
PurchaseEntity purchaseEntity = new PurchaseEntity();
// 状态设置为新建
purchaseEntity.setStatus(WareConstant.PurchaseStatusEnum.CREATED.getCode());
purchaseEntity.setCreateTime(new Date());
purchaseEntity.setUpdateTime(new Date());
this.save(purchaseEntity);
// 拿到最新的采购单id
purchaseId = purchaseEntity.getId();
}
//TODO 确认采购是 0 或 1 才可以合并
// 拿到合并项 **采购需求的id**
List<Long> items = mergeVo.getItems();
Long finalPurchaseId = purchaseId;
List<PurchaseDetailEntity> collect = items.stream().map(i -> {
// 采购需求
PurchaseDetailEntity detailEntity = new PurchaseDetailEntity();
// 通过采购单id 查询到 采购信息对象
PurchaseEntity byId = this.getById(finalPurchaseId);
// 状态如果是正在采购
if (! (byId.getStatus() == WareConstant.PurchaseDetailStatusEnum.BUYING.getCode())) {
// 设置为已分配
detailEntity.setStatus(WareConstant.PurchaseDetailStatusEnum.HASERROR.getCode());
}
detailEntity.setId(i);
// 设置采购单id
detailEntity.setPurchaseId(finalPurchaseId);
return detailEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// id批量更新
purchaseDetailService.updateBatchById(collect);
// 再次合并的话 更新修改时间
PurchaseEntity purchaseEntity = new PurchaseEntity();
purchaseEntity.setId(purchaseId);
purchaseEntity.setUpdateTime(new Date());
this.updateById(purchaseEntity);
}总结业务流程:
- 从 参数 mergeVo中取出 purchaseId 和 items 进行相关操作
- 主要是用来操作两张表
wms_purchase和wms_purchase_detail wms_purchase表是 采购信息wms_purchase_detail表是 采购需求- 我的理解是将
wms_purchase的id插入到wms_purchase_detail表中 也就是 purchase_id 字段,中间通过这个字段关联起来,同时wms_purchase表对 status 状态有比较多的选择,视频里面也是定义了两个常量
public class WareConstant {
public enum PurchaseStatusEnum{
CREATED(0,"新建"),ASSIGNED(1,"已分配"),
RECEIVE(2,"已领取"),FINISH(3,"已完成"),
HASERROR(4,"有异常");
private int code;
private String msg;
PurchaseStatusEnum(int code,String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
public enum PurchaseDetailStatusEnum{
CREATED(0,"新建"),ASSIGNED(1,"已分配"),
BUYING(2,"正在采购"),FINISH(3,"已完成"),
HASERROR(4,"采购失败");
private int code;
private String msg;
PurchaseDetailStatusEnum(int code,String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
}将常量抽取出来,修改更加方便
14.3.2 领取采购单
具体需求:
合并采购需求成功后,具体这个功能有啥用啊? 你总得需要有人去采购吧? 所以就会有一个采购APP 工作人员点击采购,然后就去采购,这里就没有实现采购 APP 就用接口来实现,通过 JSON 的参数 来请求

Controller
/**
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/received")
public R received(@RequestBody List<Long> ids) {
purchaseService.received(ids);
return R.ok();
}Service
@Override
public void received(List<Long> ids) {
// 1、确认当前采购单是 新建或者 已分配状态 才能进行采购
List<PurchaseEntity> collect = ids.stream().map(id -> {
// 根据采购id查询出采购信息
PurchaseEntity byId = this.getById(id);
return byId;
}).filter(item -> {
// 新建或者已分配留下
if (item.getStatus() == WareConstant.PurchaseStatusEnum.CREATED.getCode() ||
item.getStatus() == WareConstant.PurchaseStatusEnum.ASSIGNED.getCode()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}).map(item -> {
// 设置为已领取
item.setStatus(WareConstant.PurchaseStatusEnum.RECEIVE.getCode());
item.setUpdateTime(new Date());
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 2、改变采购单状态
this.updateBatchById(collect);
// 3、改变采购项的状态
collect.forEach((item) -> {
// 根据 purchase_id 查询出采购需求
List<PurchaseDetailEntity> entities = purchaseDetailService.listDetailByPurchaseId(item.getId());
//
List<PurchaseDetailEntity> detailEntites = entities.stream().map(entity -> {
PurchaseDetailEntity detailEntity = new PurchaseDetailEntity();
detailEntity.setId(entity.getId());
// 设置状态正在采购
detailEntity.setStatus(WareConstant.PurchaseDetailStatusEnum.BUYING.getCode());
return detailEntity;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// id批量更新
purchaseDetailService.updateBatchById(detailEntites);
});
}总结业务流程:
业务分析
- 采购人员通过 APP 点击采购 完成对应的采购需求,这里使用的是 PostMan 来发送请求,发送请求 带的参数是什么? 参数就是 采购Id
- 通过采购 Id 查询出采购相关信息,然后设置采购表的状态,设置成采购成功,同时通过这个 id 在
wms_purchase_detail表中 对应的是 purchase_id 查询采购需求表的数据, 查询到后将他的状态设置成 “正在采购“
14.3.3 完成采购
具体需求:
采购人员参与采购后,采购就会有他的结果,采购成功、采购失败,

有了请求参数,如果比较多,那么底考虑设计一个 VO 哦
@PostMapping("/done")
public R finish(@RequestBody PurchaseDoneVo doneVo) {
purchaseService.done(doneVo);
return R.ok();
}Vo
@Data
public class PurchaseDoneVo {
/**
* 采购单id
*/
@NotNull
private Long id;
public List<PurchaseItemDoneVo> items;
}@Data
public class PurchaseItemDoneVo {
/**
* 完成/失败的需求详情
*/
private Long itemId;
/**
* 状态
*/
private Integer status;
private String reason;
}Service
@Transactional
@Override
public void done(PurchaseDoneVo doneVo) {
// 采购单id
Long id = doneVo.getId();
// 2、改变采购项目的状态
Boolean flag = true;
List<PurchaseItemDoneVo> items = doneVo.getItems();
List<PurchaseDetailEntity> updates = new ArrayList<>();
for (PurchaseItemDoneVo item : items) {
PurchaseDetailEntity detailEntity = new PurchaseDetailEntity();
// 如果采购失败
if (item.getStatus() == WareConstant.PurchaseDetailStatusEnum.HASERROR.getCode()) {
flag = false;
detailEntity.setStatus(item.getStatus());
} else {
// 3、将成功采购的进行入库
PurchaseDetailEntity entity = purchaseDetailService.getById(item.getItemId());
wareSkuService.addStock(entity.getSkuId(),entity.getWareId(),entity.getSkuNum());
detailEntity.setStatus(WareConstant.PurchaseDetailStatusEnum.FINISH.getCode());
}
detailEntity.setId(item.getItemId());
updates.add(detailEntity);
}
// 批量更新
purchaseDetailService.updateBatchById(updates);
// 1、改变采购单状态
PurchaseEntity purchaseEntity = new PurchaseEntity();
purchaseEntity.setId(id);
// 设置状态根据变量判断
purchaseEntity.setStatus(flag?WareConstant.PurchaseStatusEnum.FINISH.getCode():WareConstant.PurchaseStatusEnum.HASERROR.getCode());
purchaseEntity.setUpdateTime(new Date());
this.updateById(purchaseEntity);
}addStock方法
@Override
public void addStock(Long skuId, Long wareId, Integer skuNum) {
// 先根据 skuId 和 ware_id 查询 是否拥有这个用户
List<WareSkuEntity> wareSkuEntities = wareSkuDao.selectList(new QueryWrapper<WareSkuEntity>().eq("sku_id", skuId).eq("ware_id", wareId));
//没有这个用户 那就新增
if(wareSkuEntities == null || wareSkuEntities.size() == 0) {
WareSkuEntity wareSkuEntity = new WareSkuEntity();
// 根据属性值设置
wareSkuEntity.setSkuId(skuId);
wareSkuEntity.setStock(skuNum);
wareSkuEntity.setWareId(wareId);
wareSkuEntity.setStockLocked(0);
// TODO 远程查询sku的名字 如果失败整个事务不需要回滚
try {
// 远程调用 根据 skuid进行查询
R info = productFeignService.info(skuId);
Map<String,Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) info.get("skuInfo");
if (info.getCode() == 0) {
wareSkuEntity.setSkuName((String) map.get("skuName"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
wareSkuDao.insert(wareSkuEntity);
}else {
// 有该记录那就进行更新
wareSkuDao.addStock(skuId,wareId,skuNum);
}
}addStock 具体实现
<insert id="addStock">
UPDATE `wms_ware_sku` SET stock=stock+#{skuNum} WHERE sku_id=#{skuId} AND ware_id=#{wareId}
</insert>14.3.4 Spu规格维护
具体需求:
前端项目遇到的问题: 需要自己去 router目录下找到 index.js 增加改行配置,主要是配置规格维护的路径

在 Spu管理上 点击规格后查询出相关规格信息

Controller
@GetMapping("/base/listforspu/{spuId}")
public R baseAttrListforspu(@PathVariable("spuId") Long spuId) {
List<ProductAttrValueEntity> productAttrValueEntity = productAttrValueService.baseAttrListforspu(spuId);
return R.ok().put("data",productAttrValueEntity);
}Service
@Override
public List<ProductAttrValueEntity> baseAttrListforspu(Long spuId) {
// 1、根据spuid进行查询
List<ProductAttrValueEntity> attrValueEntities = this.baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<ProductAttrValueEntity>().eq("spu_id", spuId));
return attrValueEntities;
}总结业务流程:
单表操作,根据 spu_id 查询出 pms_product_attr_value 表的信息
14.3.5 Spu更新操作
具体需求:
根据spu_id 查询出规格信息后 ,修改对应信息 提交后会发送一个post请求,并同时带上请求参数
[{
"attrId": 7,
"attrName": "入网型号",
"attrValue": "LIO-AL00",
"quickShow": 1
}, {
"attrId": 14,
"attrName": "机身材质工艺",
"attrValue": "玻璃",
"quickShow": 0
}, {
"attrId": 16,
"attrName": "CPU型号",
"attrValue": "HUAWEI Kirin 980",
"quickShow": 1
}]刚好这四个参数和实体类的一致,就不需要创建 Vo来接收

Controller
@RequestMapping("/update/{spuId}")
//@RequiresPermissions("product:attr:update")
public R updateSpuAttr(@PathVariable("spuId") Long spuId,
@RequestBody List<ProductAttrValueEntity> productAttrValueEntityList){
productAttrValueService.updateSpuAttr(spuId,productAttrValueEntityList);
return R.ok();
}Service
/**
* 先删除 后更新
* @param spuId
* @param productAttrValueEntityList
*/
@Override
public void updateSpuAttr(Long spuId, List<ProductAttrValueEntity> productAttrValueEntityList) {
// 1、根据spuid删除记录
this.baseMapper.delete(new QueryWrapper<ProductAttrValueEntity>().eq("spu_id",spuId));
// 2、遍历传递过来的记录 设置 spuId
List<ProductAttrValueEntity> collect = productAttrValueEntityList.stream().map(item -> {
item.setSpuId(spuId);
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 3、批量保存
this.saveBatch(collect);
}总结业务流程:
- 更新操作,根据前端传递过来的参数来进行更新,前端传递了一个
spu_id和多个 spu属性值 一个spu_id对多个 spu 属性值 - 先根据
spu_id删除存在 pms_product_attr_value 表的记录 - 然后对多个 ProductAttrValueEntity 对象设置 sup_id ,最后进行批量保存
分布式基础篇总结
1、分布式基础概念
- 微服务、注册中心(Nacos)、配置中心(Nacos Cofig)、远程调用、Feign、网关
2、基础开发
- SpringBoot2.0、SpringCloud、Mybatis-Plus、Vue组件化、阿里云对象存储
3、环境
- Vagrant、Linux、Docker、MySQL、Redis、逆向工程&人人开源
4、开发规范
- 数据效验JSR303、全局异常处理、全局统一返回、全家跨越处理
- 枚举状态、业务状态、VO与TO与PO划分、逻辑删除
- Lombok:@Data、@Slf4j